Effects of lipid-lowering agents on plasma lipid profile and apolipoprotein B in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus
Keywords:
T2DM, Dyslipidaemia, Cardiovascular Diseases, Apolipoprotein B-100, NigeriaAbstract
Objectives: Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus (T2DM) accounts for about 90% of all cases of Diabetes Mellitus. Dyslipidaemia has been demonstrated to form a synergy with T2DM as risk factors for cardiovascular events. This study aimed to determine the plasma levels of Lipids and Apolipoprotein B-100 among Type 2 Diabetic patients, assess the effects of Lipid Lowering agents, and to study the relationship, if any, between these lipid parameters and glycemic control.
Methods: One hundred and fifty participants consisting of fifty T2DM patients on a lipid-lowering agent, fifty newly diagnosed T2DM patients who are drug naïve (not on any anti-diabetic agent) and fifty apparently healthy non-diabetic controls were recruited for this study. Fasting blood samples were collected from all study participants for determination of Total Cholesterol (TC), LDL-C, Triglycerides (TG), High-Density Lipoprotein (HDL-C) and Apo B-100.
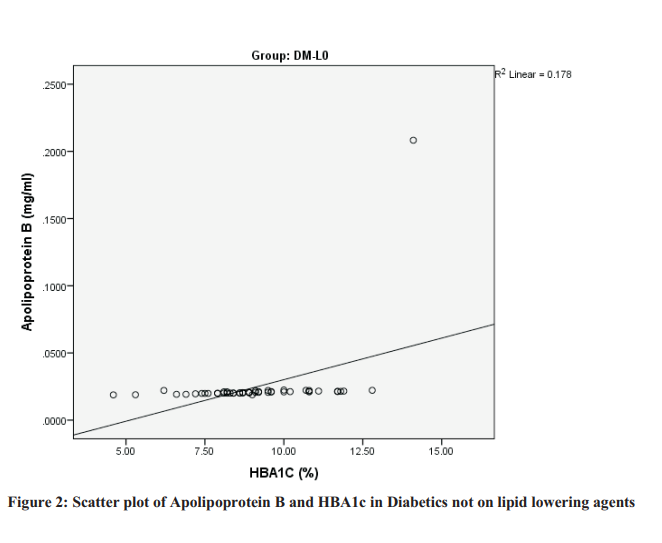
Results: The results showed significant increases in plasma TC, LDL-C, TG and Apo B-100 with a remarkable reduction in plasma HDL-C level in the Type 2 Diabetic drug naïve group compared with the treatment and control groups. There was a significant positive correlation observed between serum Apo B-100 and level of glycaemia in the T2DM drug naïve group.
Conclusion: This study further confirms the therapeutic benefits of lipid-lowering agents in reducing Apo B-100 among T2DM patients. Furthermore, maintaining good glycaemic control reduces the risk for the development of dyslipidaemia.
References
Paneni F, Beckman JA, Creager MA, Cosentino F. Diabetes and vascular disease: Pathophysiology, clinical consequences, and medical therapy: Part i [Internet]. Vol. 34, European Heart Journal. Oxford University Press; 2013. p. 2436–46.
Wright AK, Kontopantelis E, Emsley R, Buchan I, Sattar N, Rutter MK, et al. Life expectancy and cause-specific mortality in type 2 diabetes: A population-based cohort study quantifying relationships in ethnic subgroups. Diabetes Care 2017;40(3):338–45.
Morrish NJ, Wang SL, Stevens LK, Fuller JH, Keen H. Mortality and causes of death in the WHO multinational study of vascular disease in diabetes. Diabetologia 2001;44:S14–21.
Chehade JM, Gladysz M, Mooradian AD. Dyslipidemia in type 2 diabetes: Prevalence, pathophysiology, and management. Drugs 2013;73(4):327–39.
Ogbera AO, Fasanmade OA, Chinenye S,
Akinlade A. Characterization of lipid parameters in diabetes mellitus - A Nigerian report. Int Arch Med 2009;2(1):19.
Okafor C, Fasanmade O, Oke D. Pattern of dyslipidaemia among Nigerians with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Niger J Clin Pract 2008;11(1):25–31.
Wing RR, Lang W, Wadden TA, Safford M, Knowler WC, Bertoni AG, et al. Benefits of modest weight loss in improving cardiovascular risk factors in overweight and obese individuals with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care
;34(7):1481–6.
Fazio S, Shapiro MD. Apolipoprotein Bcontaining lipoproteins and atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease [Internet]. Vol. 6, F1000Research. Faculty of 1000 Ltd; 2017.
Morita SY. Metabolism and modification of apolipoprotein B-containing lipoproteins involved in dyslipidemia and atherosclerosis. Vol. 39, Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin. Pharmaceutical Society of Japan; 2016. p. 1–24.
Adaja T, Ojo M, Ayina C. Chapter 6 - Relationship of Apolipoprotein B-100 and Lipid Profile Parameters among Diabetic Patients in a Tertiary Hospital in Nigeria. In: Current Trends in Disease and Health Vol 2 2019. p. 75–84.
Sonuga OO, Abbiyesuku FM, Adedapo KS, Sonuga AA. Insulin Resistance Index and Proatherogenic Lipid Indices in the Offspring of People with Diabetes. Int J Diabetes Metab 2019;25(1–2):11–8.
Meikle PJ, Wong G, Tan R, Giral P, Robillard P, Orsoni A, et al. Statin action favors normalization of the plasma lipidome in the atherogenic mixed dyslipidemia of MetS: Potential relevance to statin-associated dysglycemia. J Lipid Res 2015;56(12):2381–92.
Baigent C, Blackwell L, Emberson J, Holland LE, Reith C, Bhala N, et al. Efficacy and safety of more intensive lowering of LDL cholesterol: A metaanalysis of data from 170 000 participants in 26 r a n d o m i s e d t r i a l s . L a n c e t
;376(9753):1670–81.
Lamon-Fava S, Diffenderfer MR, Barrett PHR, Buchsbaum A, Matthan NR, Lichtenstein AH, et al. Effects of different doses of atorvastatin on human apolipoprotein B-100, B-48, and A-I metabolism. J Lipid Res 2007;48(8):1746–53.
Hadaegh F, Shafiee G, Azizi F. Anthropometric predictors of incident type 2 diabetes mellitus in Iranian women. Ann Saudi Med 2009;29(3):194.
Yang J, Wang F, Wang J, Han X, Hu H, Yu C, et al. Using different anthropometric indices to assess prediction ability of type 2 diabetes in elderly population: A 5 year prospective study. BMC Geriatr 2018;18(1):218.
Grappin M, Piroth L, Verges B, Sgro C, Mack G, Buisson M, et al. Increased prevalence of subclinical hypothyroidism in HIV patients treated with highly active antiretroviral therapy. AIDS 2000;14(8):1070–2.
Taskinen MR. Diabetic dyslipidaemia: From basic research to clinical practice [Internet]. Vol. 46, Diabetologia. Diabetologia; 2003. p. 733–49.
Wang J, Stanèáková A, Soininen P, Kangas AJ, Paananen J, Kuusisto J, et al. Lipoprotein subclass profiles in individuals with varying degrees of glucose tolerance: A population-based study of
3 9 9 F i n n i s h m e n . J I n t e r n M e d
;272(6):562–72.
Stolinski M, Alam S, Jackson NC, ShojaeeMoradie F, Pentecost C, Jefferson W, et al. Effect of 6-month supervised exercise on low-density lipoprotein apolipoprotein B kinetics in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Metabolism 2008;57(11):1608–14.
Duvillard L, Florentin E, Lizard G, Petit JM, Galland F, Monier S, et al. Cell surface expression of LDL receptor is decreased in type 2 diabetic patients and is normalized by insulin therapy. Diabetes Care 2003;26(5):1540–4.
Ko SH, Cha BY. Diabetic peripheral neuropathy in type 2 diabetes mellitus in Korea [Internet]. Vol. 36, Diabetes and Metabolism Journal. Korean Diabetes Association; 2012. p. 6–12.
Rabbani N, Chittari MV, Bodmer CW, Zehnder D, Ceriello A, Thornalley PJ. Increased glycation and oxidative damage to apolipoprotein B100 of LDL cholesterol in patients with type 2 diabetes and e f f e c t o f m e t f o r m i n . D i a b e t e s
;59(4):1038–45.
Makita T, Tanaka A, Nakano T, Nakajima K, Numano F. Importance of glycation in the acceleration of low density lipoprotein (LDL) uptake into macrophages in patients with diabetes mellitus. Int Angiol 1999;18(2):149–53.
McTaggart F, Jones P. Effects of statins on highdensity lipoproteins: A potential contribution to cardiovascular benefit [Internet]. Vol. 22, Cardiovascular Drugs and Therapy. Springer; 2008. p. 321–38.
Barter P. Options for therapeutic intervention: How effective are the different agents? Eur Hear Journal, Suppl 2006;8(F):F47–53.
How to cite this article:
Adiels M, Borén J, Caslake MJ, Stewart P, Soro A, Westerbacka J, et al. Overproduction of VLDL1 driven by hyperglycemia is a dominant feature of diabetic dyslipidemia. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 2005;25(8):1697–703.
Chirieac D V., Collins HL, Cianci J, Sparks JD, Sparks CE. Altered triglyceride-rich lipoprotein production in Zucker diabetic fatty rats. Am J Physiol - Endocrinol Metab 2004;287(1 501):42–9.
Sierra-Johnson J, Somers VK, Kuniyoshi FHS, Garza CA, Isley WL, Gami AS, et al. Comparison of Apolipoprotein-B/Apolipoprotein-AI in Subjects With Versus Without the Metabolic Syndrome. Am J Cardiol 2006;98(10):1369–73.
Wallenfeldt K, Bokemark L, Wikstrand J, Hulthe J, Fagerberg B. Apolipoprotein B/apolipoprotein A-I in relation to the metabolic syndrome and change in carotid artery intima-media thickness during 3 years in middle-aged men. Stroke 2004;35(10):2248–52.
Mallick AK, Maradi R, Joshi VR, Bhat PG. A Study on Apo B100 / Apo a-I Ratio in
Uncontrolled Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Int J Appl Biol Pharm Technol 2011;2(1):379–84.
Hwang YC, Ahn HY, Kim WJ, Park CY, Park SW. Increased apoB/A-I ratio independently associated with Type 2 diabetes mellitus: crosssectional study in a Korean population. Diabet Med 2012;29(9):1165–70.
Mora S, Otvos JD, Rosenson RS, Pradhan A, Buring JE, Ridker PM. Lipoprotein particle size and concentration by nuclear magnetic resonance and incident type 2 diabetes in women. Diabetes
;59(5):1153–60
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2023 Research Journal of Health Sciences

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
Research Journal of Health Sciences journal is a peer reviewed, Open Access journal. The Journal subscribed to terms and conditions of Open Access publication. Articles are distributed under the terms of Creative Commons License (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0). (http://creativecommons.org/licences/by-nc-nd/4.0). All articles are made freely accessible for everyone to read, download, copy and distribute as long as appropriate credit is given and the new creations are licensed under the identical terms.

