Blended teaching and learning methods in nursing and midwifery education: A scoping review of the literature
Keywords:
Blended learning, nursing and midwifery education, SSA, RwandaAbstract
Background: Blended learning (BL) is defined as the combination of both traditional face-to-face learning and synchronous or asynchronous e-learning approaches. The aim of this scoping review was to explore the literature to obtain a broad understanding of the use of BL in nursing and midwifery education in general, in Sub-Saharan Africa (SSA), and in particular Rwanda.
Methods: The literature published between 2010 and 2019 were reviewed from six electronic databases using keywords including blended learning, nursing education, midwifery education, higher education, SSA, and Rwanda. Arksey and O'Malley's framework was used in this review.
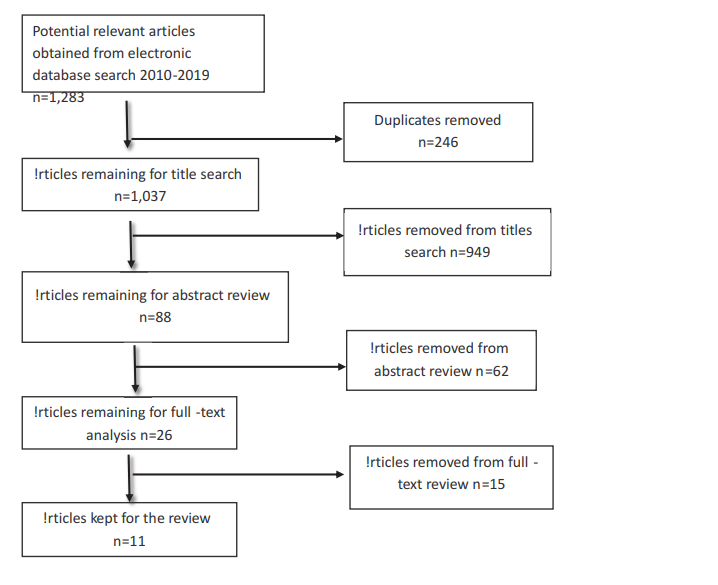
Results: The initial search identified 1,283 records. Eleven articles were selected for this review after the application of predetermined inclusion criteria. Almost all reviewed articles indicated that the integration of BL methods improved the quality of nursing and midwifery education in general, and in SSA countries including Rwanda.
Conclusions: Initial research in this area highlights that moving from traditional classroom-delivered programs to the BL approach is feasible and can promote the quality of nursing and midwifery standards of education. This scoping review highlights a paucity of research on BL in nursing and midwifery education, particularly in SSA countries.
References
Fukada M. Nursing competency: Definition, structure and development. Yonago Acta Medica. 2018.
Leung K, Trevena L, Waters D. Development of a competency framework for evidence-based
practice in nursing. Nurse Educ Today. 2016;
Makhdoom N, Khoshhal KI, Algaidi S, Heissam K, Zolaly MA. “Blended learning” as an effective teaching and learning strategy in clinical medicine: A comparative cross-sectional university-based study. J Taibah Univ Med Sci [Internet]. 2013;8(1):12–7. Available from:
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jtumed.2013.01.002
O'Flaherty J, Phillips C. The use of flipped classrooms in higher education: A scoping review. Internet High Educ [Internet]. 2015;25(February
0 1 5 ) : 8 5 – 9 5 . A v a i l a b l e f r o m :
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.iheduc.2015.02.002
Blackboard Inc. Educational benefits of online learning. www.blackboard.net [Internet].
0 0 0 ; 1 – 6 . A v a i l a b l e f r o m :
http://blackboardsupport.calpoly.edu/content/fac ulty/handouts/Ben_Online.pdf
Mccutcheon K, Lohan M, Traynor M, Martin D. A systematic review evaluating the impact of online or blended learning vs. face-to-face learning of clinical skills in undergraduate nurse education. J Adv Nurs. 2015;71(2):255–70.
Sadeghi R, Sedaghat MM, Sha Ahmadi F.
Comparison of the effect of lecture and blended teaching methods on students' learning and satisfaction. J Adv Med Educ Prof [Internet].
;2(4):146–50. Available from: http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender. fcgi?artid=4235559&tool=pmcentrez&rendertyp e=abstract
Balasubramaniam SM, Bhargava S, Agrawal N, Asif R, Chawngthu L, Sinha P, et al. Blending virtual with conventional learning to improve student midwifery skills in India. Nurse Educ Pract. 2018;28(October 2017):163–7.
Protsiv M, Rosales-Klintz S, Bwanga F,
Zwarenstein M, Atkins S. Blended learning across universities in a South-North-South collaboration: A case study. Heal Res Policy Syst [Internet].
0 1 6 ; 1 4 ( 1 ) : 1 – 1 2 . Av a i l a b l e f r o m :
http://dx.doi.org/10.1186/s12961-016-0136-x
Kaur M. Blended learning - its challenges and future. Procedia - Soc Behav Sci [Internet].
0 1 3 ; 9 3 : 6 1 2 – 7 . Av a i l a b l e f r o m :
http://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S1877
X
Nazarenko AL. Blended learning vs traditional learning: What works? (A Case study research).
Procedia - Soc Behav Sci [Internet]. 2015;200(October):77–82. Available from: http://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S1877
Güzer B, Caner H. The past, present and future of blended learning: An in depth analysis of literature. Procedia Soc Behav Sci [Internet]. 2014;214(1):4596–603. Available from:
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.sbspro.2014.01.992
Vaona A, Banzi R, Kh K, Rigon G, Cereda D, Pecoraro V, et al. E-learning for health professionals ( Review ). Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018;(1).
Kotoua S, Ilkan M, Kilic H. The growing of online education in Sub Saharan Africa: Case study Ghana. Procedia - Soc Behav Sci [Internet]. 2015;191:2406–11. Available from:
http://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S1877
Harerimana A, Mtshali NG, Hewing H,
Kyamusoke EB, Mukankaka A, Gasurira S, et al. E-Learning in nursing education in Rwanda?: Benefits and challenges . An Exploration of participants ' perceptives. J Nurs Heal Sci. 2016;5(2):64–92.
Liu Q, Peng W, Zhang F, Hu R, Li Y, Yan W. The effectiveness of blended learning in health professions: Systematic review and metaanalysis. J Med Internet Res. 2016;18(1):e2.
Li Z, Tsai M-H, Tao J, Lorentz C. Switching to blended learning: The impact on students' academic performance. J Nurs Educ Pract [Internet]. 2014;4(3):245–51. Available from: http://www.sciedu.ca/journal/index.php/jnep/arti cle/view/3477
Soper T. Knowledge into learning: comparing lecture, e-learning and self-study take-home packet instructional methodologies with nurses. Nurs Open [Internet]. 2017;4(2):76–83. Available from: http://doi.wiley.com/10.1002/nop2.73
Kenney J, Newcombe E. Adopting a blended learning approach: Challenges encountered and lessons learned in an action research study. J
Asynchronous Learn Netw [Internet]. 2011;15(1):45–57. Available from:
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.sbspro.2014.01.992
Mukama E. Baseline study of the status of opne and distance learning in Rwanda. 2016;38. Available from: www.col.org
Zolfaghari M, Negarandeh R, Eybpoosh S. Developing a blended learning program for nursing and midwifery students in Iran: Process and preliminary outcomes. Iran J Nurs Midwifery Res. 2013;18(1):20–6.
Eghbalibabadi M, Ashouri E. Comparison of the effects of two teaching methods on the nursing students ' performance in measurement of blood pressure. Iran J Nurs Midwifery Res [Internet].
0 1 4 ; 1 9 ( 4 ) : 3 – 7 . Av a i l a b l e f r o m : https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC
/
Arksey H, O'Malley L. Scoping studies?: Towards a methodological framework. Int J Soc Res Methodol. 2005;8(1):19–32.
Armstrong R, Hall BJ, Doyle J, Waters E. “Scoping the scope” of a cochrane review. J Public Health (Bangkok). 2011;33(1):147–50.
Levac D, Colquhoun H, O'Brien KK. Scoping studies: Advancing the methodology. Implement Sci. 2010;5(1):1–9.
Sweeney MR, Kirwan A, Kelly M, Corbally M, O Neill S, Kirwan M, et al. Transition to blended learning: experiences from the first year of our blended learning Bachelor of Nursing Studies programme. Contemp Nurse. 2016;52(5):612–24.
Young N, Randall J. The use of blended learning to create a module about ill-health during childbirth for pre-registration midwifery students. Nurse
Educ Pract [Internet]. 2014;14(1):87–91.
A v a i l a b l e f r o m :
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.nepr.2013.02.016
Mary S, Julie J, Jennifer G. Teaching evidence based practice and research through blended learning to undergraduate midwifery students from a practice based perspective. Nurse Educ Pract [Internet]. 2014;14(2):220–4. Available f r o m :
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.nepr.2013.10.001
Mulaudzi FM, Chyun DA. Innovation in Nursing and Midwifery Education and Research. Rwanda Journa Ser F Med Heal Sci. 2015;2(2).
Harerimana A, Mtshali NG, Hewing H,
Kyamusoke EB, Mukankaka A, Gasurira S, et al. E-Learning in Nursing Education in Rwanda?: Benefits and Challenges . An Exploration of Participants ' Perceptives. J Nurs Heal Sci. 2016;5(2):64–92.
Creedon SA, Cummins AM. Development of a blended model of teaching and learning for nursing students on rostered placement to ensure competence in information and communication technology for professional practice in Ireland.
C I N - C o m p u t I n f o r m a t i c s N u r s .
;30(5):274–9.
Bergström P, Lindh V. Developing the role of Swedish advanced practice nurse (APN) through a blended learning master's program:
Consequences of knowledge organisation. Nurse
Educ Pract [Internet]. 2018;28(October 2 0 1 7 ) : 1 9 6 – 2 0 1 . Av a i l a b l e f r o m :
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nepr.2017.10.030
Appiagyei M, Trump A, Danso E, Yeboah A, Searle S, Carr C. Case study: The role of elearning in midwifery pre-service education in
Ghana. World Heal Popul [Internet]. 2015;16(2):54–61. Available from: https://www.longwoods.com/content/24492
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2023 Research Journal of Health Sciences

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
Research Journal of Health Sciences journal is a peer reviewed, Open Access journal. The Journal subscribed to terms and conditions of Open Access publication. Articles are distributed under the terms of Creative Commons License (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0). (http://creativecommons.org/licences/by-nc-nd/4.0). All articles are made freely accessible for everyone to read, download, copy and distribute as long as appropriate credit is given and the new creations are licensed under the identical terms.

