Awareness and knowledge about diabetes mellitus and hypertension amongst adolescents in secondary schools, Oyo State, Nigeria – an interventional Study by the +SIDCAIN Research Group
Keywords:
Awareness, knowledge, diabetes, hypertension, adolescentsAbstract
Background: Epidemic of obesity has propelled type 2 diabetes into an emerging health problem. Alongside hypertension, diabetes is now a foremost non communicable disease (NCD) in Nigeria.
Aims & Objectives: This paper reports the outcome of school health club awareness program amongst school children in Oyo State.
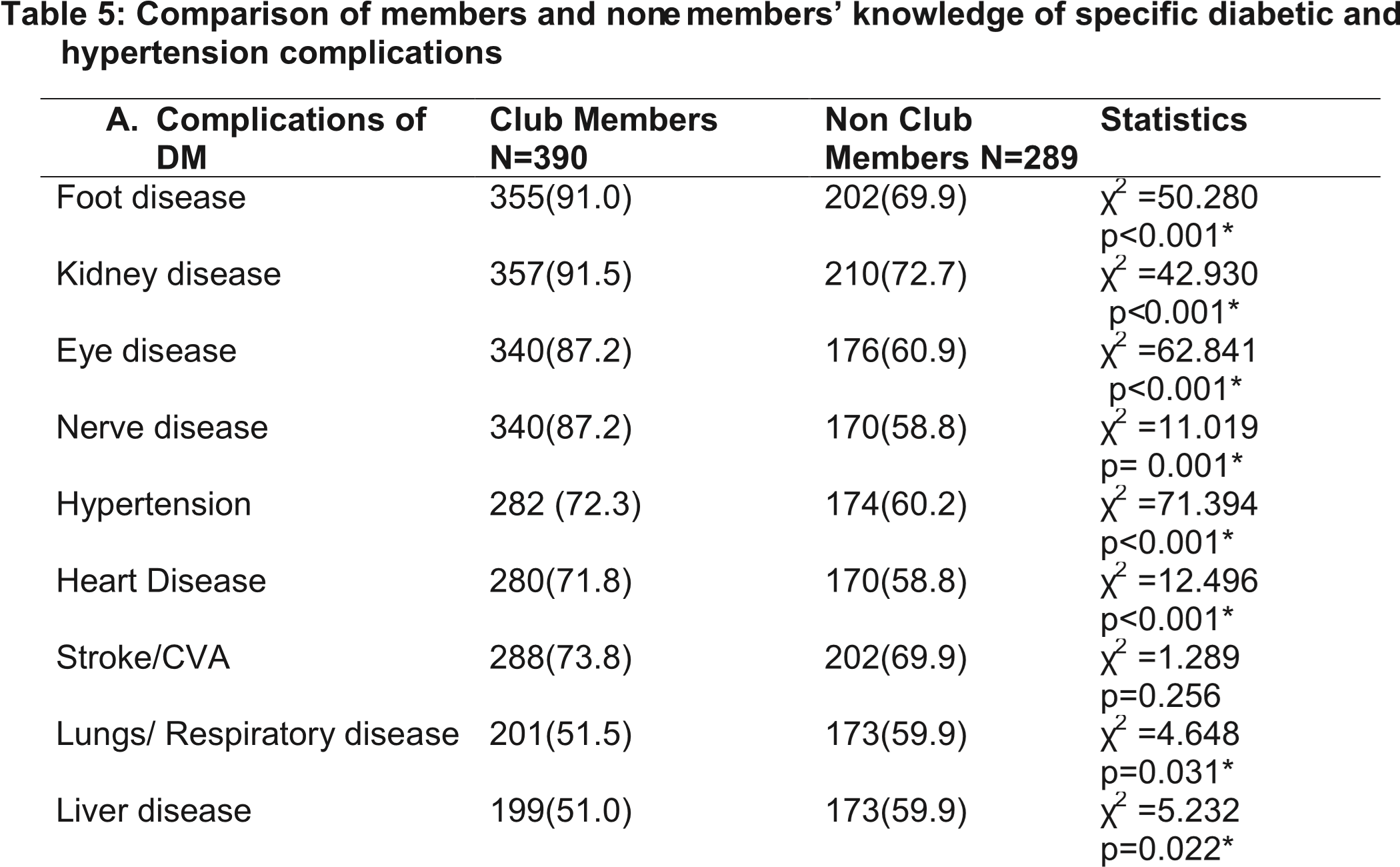
Methods: Health clubs were formed with the aim of making adolescents aware of NCDs, and their risk factors through health educational programs over a three year period (2010 – 2013). Data was obtained on awareness, knowledge, and traditional beliefs amongst club members and compared to responses from non-club members. SPSS version 17 was used for data analysis, and the level of statistical significance was set at (p<0.05).
Results: A total of 894 respondents were recruited with 456 (51%) from 20 health clubs while 438 (49%) were non-members. Mean age was 15.67 years (± 1.25 years) with279 (31.2%) males.Obesity, family history of diabetes, decreased physical activity, and stress were adjudged to be risk factors for diabetes by 77.3%, 75.4% 63.8% and 33.4% of the total respondents respectively. For hypertension, stress, family history of diabetes, obesity, decreased physical activity, and low consumption of vegetables were adjudged to be the risk factors by 83.3%, 64.1%, 63.1%, 57.2% and 50.3% of the respondents respectively. More health club members (95.0%) were aware of diabetes than non members (81.7%). Similar results obtained for hypertension (96.9% against 84.0% respectively).There was a wide gap between the knowledge of clubs members who received education and non members who did not, p<0.05
Conclusion: Knowledge plays an essential role in the early prevention, detection and future development of a disease. There is a need to expand educational activities on NCDs through viable policies and programmes in communities where risk factors are becoming highly prevalent even among young people.
References
International Diabetes Foundation. DiabetesAtlas. Available from:
http://www.idf.org/diabetesatlas/.[Last accessed 2012, July, 2].
Chukwuonye II, Chuku A, John C, Ohagwu KA, Imoh ME, Isa SE et al. Prevalence of overweight and obesity in adult Nigerians – a systematic review. Diabetes, Metabolic Syndrome and Obesity: Targets and Therapy 2013:6 43–47.
Alebiosu C. O. Familoni O.B. Ogunsemi O. et al. Indian Journal of Edocrinology and Metabolism. Community based diabetes risk assessment in Ogun State, Nigeria (World Diabetes Foundation Project 08-321). 2013: 17(4); 646 – 651.
Mohan D, Raj D, Shanthirani CS, Datta M, Unwin NC, KapurA et al. Awareness and knowledge of diabetes mellitus in Chennai- The Chennai Urban Rural Epidemiological study (CURES 9). JAPI Vol.53. April 2005.
Al-Mahrooqi B, Al-Hadhrami R, Al-Amri
A, Al-Tamimi S, Al-Shidhani A, AlLawati H et al. Self-Reported Knowledge of Diabetes among High School Students in Al-Amerat and Quriyat, Muscat Governate, Oman. Sultan QaboosUniv Med J. 2013 August; 13(3): 392–398.
Latifeh Al-Sarayra, Reem S. Khalidi. Awareness and Knowledge about
Diabetes Mellitus among Students at AlBalqa' Applied University.Pakistan J of Nutrition 2012. 11 (11): 1023-1028.
Sundar JS, Adaikalam JMS, Parameswari S, Valarmarthi S, Kalpana S, et al. (2013)
Prevalence and Determinants of Hypertension among Urban School Children in the Age Group of 13- 17 Years in, Chennai, Tamilnadu. Epidemiol 3: 130. doi:10.4172/2161-1165.1000130
Unadike BC, Chineye S. Knowledge, awareness, and impact of diabetes among adolescents in Uyo, Nigeria. African J Diabetes Med. 2009:12–14.
World Health Organization. Global status report on non-communicable diseases. 2010.
World Health Organization. Obesity: preventing and managing the global epidemic; report of a WHO consultation on obesity. Geneva,2000.
Rena IK, Demosthenes BP. The epidemic of obesity in children and adolescents in the world. Cent Eur J Publ Health 2006; 14 (4): 151-159.
Al-Shafaee M, Al-Shukaili S, Rizvi S, Al- Farsi Y, Khan M, Ganguly S, et al. Knowledge and perceptions of diabetes in a semi-urban Omani population. BMC Public Health. 2008;8:249.
Khan N, Gomathi KG, Shehnaz SI,
Muttappallymyalil J. Diabetes MellitusRelated Knowledge among University Students in Ajman, United Arab Emirates. Sultan QaboosUniv Med J. 2012 August; 12(3): 306–314.
Mohieldein AH, Al Zohairy MA, Hasan M. Awareness of diabetes mellitus among
Saudi non-diabetic population in AlQassim region, Saudi Arabia. J Diabetes Endocrinol. 2011;2:14–19.
Wee HL, Ho HK, Li SC. Public awareness of diabetes mellitus in Singapore. Singapore Med J. 2002;43:128–34.
Cullen KW, Buzek BB. Knowledge about type 2 diabetes risk and prevention of African-American and Hispanic adults
and adolescents with family history of type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Educ. 2009;35:836–42.
Oladapo O.O, Salako L, Sadiq L, Soyinka
K, Falase A.O. Knowledge of
Hypertension and other Risk Factors for Heart Disease among Yoruba Rural Southwestern Nigerian Population. British Journal of Medicine & Medical Research 2013; 3(4): 993-1003.
Shaikh MA, Yakta D, Sadia, Raj Kumar.
Hypertension Knowledge, Attitude and
Practice in Adult Hypertensive Patients at Liaquat University of Medical and
Health Sciences JLUMHS 2012; 11
(02): 113-116.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2023 Research Journal of Health Sciences

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
Research Journal of Health Sciences journal is a peer reviewed, Open Access journal. The Journal subscribed to terms and conditions of Open Access publication. Articles are distributed under the terms of Creative Commons License (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0). (http://creativecommons.org/licences/by-nc-nd/4.0). All articles are made freely accessible for everyone to read, download, copy and distribute as long as appropriate credit is given and the new creations are licensed under the identical terms.

