A retrospective assessment of rifampicin resistance in paediatric tuberculosis in a tertiary hospital in south west Nigeria
Keywords:
Tuberculosis, Rifampicin Resistance, Pediatric, otaigbei@babcock.edu.ngAbstract
Objectives: Children infected with tuberculosis, including drug resistant
tuberculosis serve as reservoirs for Tuberculosis (TB) and as indicators of recent
or ongoing transmission in the community. The aim of this study was to evaluate
the prevalence of rifampicin resistance in paediatric tuberculosis in Babcock
University Teaching Hospital, Ilishan Remo, Ogun State, Nigeria
Methodology: This was a retrospective study that involved a review of medical
microbiology laboratory records to analyze GeneXpert results of sputum
samples obtained from pediatric patients with tuberculosis between January
2017 and March 2022. Aconvenience sampling method was used to select cases
who met the study's inclusion criteria until the sample size was attained.
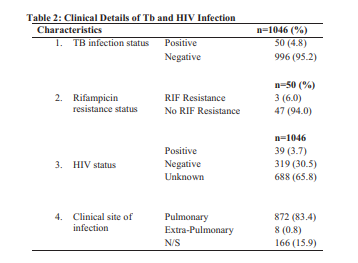
Results: The medical laboratory records of 1046 subjects were analyzed in this
study of which 556 (53.2%) were males. The mean age of all the patients was
10.77±4.38 years and majority of the respondents 445 (42.5%) were in the age
group 11-15 years. Fifty patients (4.8%) had positive GeneXpert results of
which 3 (6.0%) were Rifampicin resistant.
Conclusion: In order to lower the burden of TB globally more efforts should be
made to reduce paediatric TB.
References
Medecins Sans Frontières (MSF). MSF
Medical Guidelines. Global Burden of
T u b e r c u l o s i s .
https://medicalguidelines.msf.org/en/viewpor
t/TUB/english/1-7-global-burden-oft u b e r c u l o s i s -
html#footnote2_aee0dgi
World Health Organization. Global
Tuberculosis Report 2021. Geneva: World
H e a l t h O r g a n i z a t i o n ; 2 0 2 1 .
https://apps.who.int/iris/rest/bitstreams/13797
/retrieve
World Health Organization. Tuberculosis.
World He a lth Organi z a tion. 2020.
h t t p s : / / w w w . w h o . i n t / h e a l t h -
topics/tuberculosis#tab=tab_1.
Foo C, Shrestha P, Wang L, Du Q, GarcíaBasteiro AL, Abdullah AS, Legido-Quigley H.
I n t e g r a t i n g t u b e r c u l o s i s a n d
noncommunicable diseases care in low- and
middle-income countries (LMICs): A
systematic review. PLoS Med. 2022;19(1):1-
2 .
https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pmed.100389
.
World Health Organization. Tuberculosis.
https://www.who.int/news-room/factsheets/detail/tuberculosis
Abou JGJ, Garcia BI, Nguhiu P, Siroka A,
Palmer T, Goscé L, et al. Allel K, Sinanovic E,
Skordis J, Haghparast-Bidgoli H. National
tuberculosis spending efficiency and its
Otaigbe et al., 2024
Res. J. Health Sci. Vol 12(1), March 2024 45
associated factors in 121 low-income and
middle-income countries, 2010-19: a data
envelopment and stochastic frontier analysis.
Lancet Glob Health. 2022 ;10(5):e649-e660.
h t t p s : / / d o i . o r g / 1 0 . 1 0 1 6 / S 2 2 1 4 -
X(22)00085-7
Chowdhury K, Ahmad R, Sinha S, Dutta S,
Haque M. Multidrug-Resistant TB (MDR-TB)
and Extensively Drug-Resistant TB (XDRTB) Among Children: Where We Stand Now.
C u r e u s . 2 0 2 3 ; 1 5 ( 2 ) : e 3 5 1 5 4 .
https://doi.org/10.7759/cureus.35154
University of Liverpool Centre of Excellence
for long-acting therapeutics.Reducing the
burden of TB in the world's most in need
communities with long-acting injectables.
https://www.liverpool.ac.uk/centre-ofe x c e l l e n c e - f o r - l o n g - a c t i n g -
therapeutics/blog/longevity-blog/reducingthe-burden-of-tb/
World Health Organization. Global
t u b e r c u l o sis r e p o r t 2 0 2 2 . 2 0 2 2
https://www.iom.int/sites/g/files/tmzbdl486/fi
les/documents/2023-03/Global-TB-Report2022.pdf
Jilani TN, Avula A, Zafar Gondal A, Siduqui
AH. Active Tuberculosis. In: StatPearls.
Treasure Island, Florida: StatPearls
P u b l i s h i n g ; p . 1 - 2 5 .
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK51
/
Dunn JJ, Starke JR, Revell PA. Laboratory
Diagnosis of Mycobacterium tuberculosis
Infection and Disease in Children. J Clin
Mi c r o b i o l. 2 0 1 6 ; 5 4 ( 6 ): 1 4 3 4 - 1 4 4 1 .
https://doi.org/10.1128/JCM.03043-15
Herchline ET, Amorosa JK. Tuberculosis.
M e d s c a p e . 2 0 2 3 .
https://emedicine.medscape.com/article/2308
-overview
Nardell EA. Tuberculosis. MSD Manuals
P r o f e s s i o n a l V e r s i o n . 2 0 2 2
https://www.msdmanuals.com/professional/in
fectious-diseases/mycobacteria/tuberculosistb
Boston University, Research Occupational
Health Program. Mycobacterium tuberculosis
a g e n t I n f o r m a t i o n s h e e t .
https://www.bu. edu/r e s e a r ch/ e thi c scompliance/safety/rohp/agent-informationsheets/mycobacterium-tuberculosis-agentinformation-sheet/
Herman P, Fauville-Dufaux M, Breyer D, Van
Vaerenbergh B, Pauwels K, Thi CDD, Sneyers
M, Wanlin M, Snacken R, Moens W. Biosafety
Recommendations for the Contained Use of
Mycobacterium tuberculosis Complex Isolates
in Industrialized Countries. Scientific Institute
of Public Health, Division of Biosafety and
B i o t e c h n o l o g y . 2 0 0 6 .
https://www.biosafety.be/sites/default/files/mt
ub_final_dl.pdf
Government of Canada.Pathogen Safety Data
Sh e e ts: I n f e c ti o u s Su b st a n c e s –
M y c o b a c t e ri u m t u b e r c u l o sis a n d
Mycobacterium tuberculosis complex.
h tt p s:// w w w. c a n a d a . c a / e n / p u b li c -
health/services/laboratory-biosafetybiosecurity/pathogen-safety-data-sheets-riskassessment/mycobacterium-tuberculosiscomplex.html
Jessenius Faculty Of Medicine in Martin.
Comenius University. Bratislava, Slovakia.
Microbiology 2 Practical: Mycobacteria.
https://www.jfmed.uniba.sk/fileadmin/jlf/Pra
c o v i s k a / u s t a v - m i k r o b i o l o g i e - a -
imunologie/distancna_vyuka/VLa_mycobact
eria.pdf
Newton SM, Brent AJ, Anderson S, Whittaker
E, Kampmann B. Paediatric tuberculosis.
Lancet Infect Dis. 2008;8(8):498-510.
h t t p s : / / d o i . o r g / 1 0 . 1 0 1 6 / S 1 4 7 3 -
(08)70182-8
Maphalle LNF, Michniak-Kohn BB,
Ogunrombi MO, Adeleke OA. Pediatric
Tuberculosis Management: A Global
Challenge or Breakthrough? Children (Basel).
0 2 2 ; 9 ( 8 ) : 1 - 4 2 .
https://doi.org/10.3390/children9081120 .
Hamzaoui A, Yaalaoui S, Tritar Cherif F, Slim
Saidi L, Berraies A. Childhood tuberculosis: a
concern of the modern world. Eur Respir Rev.
0 1 4 S e p ; 2 3 ( 1 3 3 ) : 2 7 8 - 9 1 .
https://doi.org/10.1183/09059180.00005314
Sandgren A, Cuevas LE, Dara M, Gie RP,
Grzemska M, Hawkridge A, et al. Childhood
tuberculosis: progress requires an advocacy
strategy now. Eur Respir J. 2012;40(2):294-7.
https://doi.org/10.1183/09031936.00187711
Zhuang Z, Sun L, Song X, Zhu H, Li L, Zhou
X, et al. Trends and challenges of multi-drug
resistance in childhood tuberculosis. Front Cell
Infect Microbiol. 2023 ;13 91183590): 1-7.
https://doi.org/10.3389/fcimb.2023.1183590
The Global Fund. Tuberculosis:the challenge.
0 2 3 .
https://www.theglobalfund.org/en/tuberculosi
s/
Elizabeth Glaser Paediatric Aids Foundation.
Tuberculosis: Expanding Access To Diagnosis
a n d T r e a t m e n t f o r T B . 2 0 2 3 .
https://pedaids.org/our-expertise/tuberculosis/
Kaiser Family Foundation. The U.S.
Government and Global Tuberculosis
Efforts.2023.https://www.kff.org/globalhealth-policy/fact-sheet/the-u-s-governmentand-global-tuberculosis-efforts/
United Nations. How TB infections increased
d u r i n g C O V I D -
https://www.un.org/africarenewal/magazin
e/october-2022/how-tb-infections-deathsincreased-during-covid-19-pandemic
Pan American Health Organization.
Tuberculosis deaths and disease increase
Otaigbe et al., 2024
Res. J. Health Sci. Vol 12(1), March 2024 46
during the COVID-19 pandemic. 2022.
https://www.paho.org/en/news/27-10-2022-
tuberculosis-deaths-and-disease-increaseduring-covid-19-pandemic
Uwishema O, Rai A, Nicholas A, Abbass M,
Uweis L, Arab S, et al. Childhood tuberculosis
outbreak in Africa: is it a matter of concern? Int
J Su r g . 2 0 2 3 ; 1 0 9 ( 5 ) : 1 5 3 9 - 1 5 4 2 .
https://doi.org/10.1097/JS9.00000000000001
World Health Organization Africa Region.
T u b e r c u l o s i s . 2 0 2 3 .
h tt p s:// w w w. a f r o . w h o .i n t/ h e a lt h -
topics/tuberculosis-tb
National Tuberculosis and Leprosy Control
Programme. End-Term Review of Nigeria's
National Strategic Plan For Tuberculosis
Control 2015-2020
https://ntblcp.org.ng/content/uploads/2023/06/Finalreport-ETR-NIGERIA-1.pdf
World Health Organization Africa Region.
African Union and WHO urge swift action
against childhood tuberculosis. 2022.
https://www.afro.who.int/news/african-uniona n d -wh o - u rg e -swift- a c ti o n - a g a i n stchildhood-tuberculosis
Bagcchi S. Reducing tuberculosis in African
childr en. Lanc e t Inf e c t Dis. 2022
Nov;22(11):1544. .
Federal Ministry of Health, National
Tube r culosis and Leprosy Control
Programme. 2019 Annual TB Report.
https://www.health.gov.ng/doc/Draft-2019-
NTBLCP-Annual-report-22032020.pdf
World Health Organization. WHO releases
new global lists of high-burden countries for
TB, HIV-associated TB and drug-resistant TB.
https://www.who.int/news/item/17-06-
-who-releases-new-global-lists-of-highburden-countries-for-tb-hiv-associated-tband-drug-resistant-tb
Muanya C, Onyedika-Ugoeze N. World TB
Day. Nigeria Ranks 6 among high TB Burden
Countries. The Guardian. 2023, March 24
%20the%2014,globally%20and%201st%20in
%20Africa.
KNCV Tuberculosis Foundation Nigeria. A
Major Issue With Tb In Nigeria Is The Low Tb
Case Finding For Both Adults And Children.
https://kncvnigeria.org/nigeria-isamong-the-14-high-burden-countries-for-tb/
World Health Organization Regional Office
for Gearing towards a TB free Nigeria- WHO
and partners scale up action. 2021
https://www.afro.who.int/news/gearingtowards-tb-free-nigeria-who-and-partnersscale-action
Ogbo FA, Ogeleka P, Okoro A, Olusanya BO,
Olusanya J, Ifegwu KI, et al. Tuberculosis
disease burden and attributable risk factors in
Nigeria, 1990–2016. Trop Med Health.
;46:1-11. https://doi.org/10.1186/s41182-
-0114-9
Adebowale-Tambe N. Tuberculosis: Stigma,
funding , other factors threaten disease
elimination in Nigeria. Premium times.
https://www.premiumtimesng.com/news/head
lines/519247-2022-world-tb-day-stigmapoor-funding-other-factors-threaten-diseaseelimination-in-nigeria.html
Ugwu KO, Agbo MC, Ezeonu IM. Prevalence
Of Tuberculosis, Drug-Resistant Tuberculosis
And Hiv/Tb Co-Infection In Enugu, Nigeria.
Afr J Infect Dis. 2021 ;15(2):24-30.
https://doi.org/10.21010/ajid.v15i2.5
Carvalho I, Goletti D, Manga S, Silva DR,
Manissero D, Migliori G. Managing latent
tuberculosis infection and tuberculosis in
children. Pulmonology. 2018;24(2):106-114.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rppnen.2017.10.007
Migliori GB, Nardell E, Yedilbayev A,
D'Ambrosio L, Centis R, Tadolini M, et al.
Reducing tuberculosis transmission: a
consensus document from the World Health
Organization Regional Office for Europe. Eur
R e s p i r J . 2 0 1 9 ; 5 3 ( 6 ) : 1 - 1 8 .
https://doi.org/10.1183/13993003.00391-
United States Centers for Disease Control. TB
i n c h i l d r e n . 2 0 2 3 .
https://www.cdc.gov/tb/topic/populations/tbin
children/default.htm
Thomas TA. Tuberculosis in Children. Pediatr
Clin North Am. 2017;64(4):893-909.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pcl.2017.03.010 .
Health Protection Surveillance Centre.
Guidelines on the Prevention and Control of
T u b e r c u l o s i s i n I r e l a n d 2 0 1 0 .
h t t p s : / / w w w . h p s c . i e / a -
z/vaccinepreventable/tuberculosistb/guidance
/tbguidelines2010amended2014/tb%20guidan
ce%20chapter%208.pdf
Coleman M, Martinez L, Theron G, Wood R,
Marais B. Mycobacterium tuberculosis
Transmission in High-Incidence Settings-New
Paradigms and Insights. Pathogens. 2022
; 1 1 ( 1 1 ) : 1 - 2 0 .
https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens11111228 .
Seddon JA, Shingadia D. Epidemiology and
disease burden of tuberculosis in children: a
global perspective. Infect Drug Resist.
0 1 4 ; 7 : 1 5 3 - 6 5 .
https://doi.org/10.2147/IDR.S45090
Linn AR, Dubois MM, Steenhoff AP. UnderReporting of Tuberculosis Disease among
Children and Adolescents in Low and MiddleIncome Countries: A Systematic Review. Trop
M e d I n f e c t D is. 2 0 2 3 ; 8 ( 6 ): 1 - 1 6 .
https://doi.org/10.3390/tropicalmed8060300
Joshi B, De Lima YV, Massom DM, Kaing S,
Banga MF, Kamara ET, et al. TB-Speed
Otaigbe et al., 2024
Res. J. Health Sci. Vol 12(1), March 2024 47
Decentralization study group. Acceptability of
decentralizing childhood tuberculosis
diagnosis in low-income countries with high
tuberculosis incidence: Experiences and
perceptions from health care workers in SubSaharan Africa and South-East Asia. PLOS
Glob Public Health. 2023 ;3(10):1-24.
https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pgph.0001525
An Y, Teo AKJ, Huot CY, Tieng S, Khun KE,
Pheng SH, et al. Barriers to childhood
tuberculosis case detection and management in
Cambodia: the perspectives of healthcare
providers and caregivers. BMC Infect Dis.
0 2 3 ; 2 3 ( 1 ) : 1 - 1 0 .
https://doi.org/10.1186/s12879-023-08044-y
World Health Organization Regional Office
for Africa. The African Regional Health
R e p o r t . 2 0 0 6 .
https://www.afro.who.int/sites/default/files/2
1 7 -
/african_regional_health_report2006_0.pdf
UNICEF Data. An Agenda for Action on
Tuberculosis. 2018https://data.unicef.org/wpcontent/uploads/2018/03/TB-AdvocacyBrochure-Final-3_21-high-Res.pdf
Gebremichael B, Abebaw TA, Moges T,
Abaerei AA, Worede N. Predictors of pediatric
tuberculosis in public health facilities of Bale
zone, Oromia region, Ethiopia: a case control
study. BMC Infect Dis. 2018;18(1):252.
https://doi.org/10.1186/s12879-018-3163-0
World Health Organization. Overcoming the
drug resistant TB crises in children and
a d o l e s c e n t s . 2 0 2 0
https://www.who.int/news/item/20-11-2020-
overcoming-the-drug-resistant-tb-crisis-inchildren-and-adolescents
Prestinaci F, Pezzotti P, Pantosti A.
Antimicrobial resistance: a global multifaceted
phenomenon. Pa thog Glob He a lth.
0 1 5 ; 1 0 9 ( 7 ) : 3 0 9 - 1 8 .
https://doi.org/10.1179/2047773215Y.000000
Dheda K, Gumbo T, Gandhi NR, Murray M,
Theron G, Udwadia Z, et al. Global control of
tuberculosis: from extensively drug-resistant
to untreatable tuberculosis. Lancet Respir
M e d . 2 0 1 4 ; 2 ( 4 ) : 3 2 1 - 3 8 .
h t t p s : / / d o i . o r g / 1 0 . 1 0 1 6 / S 2 2 1 3 -
(14)70031-1
Piatek AS, Van Cleeff M, Alexander H, Coggin
WL, Rehr M, Van Kampen S, Shinnick TM,
Mukadi Y. GeneXpert for TB diagnosis:
planned and purposeful implementation. Glob
Health Sci Pract. 2013;1(1):18-23.
https://doi.org/10.9745/GHSP-D-12-00004
Evans CA. GeneXpert--a game-changer for
tuberculosis control? PLoS Med. 2011
; 8 ( 7 ) : e 1 0 0 1 0 6 4 .
https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pmed.100106
World Health Organization. Largest ever rollout of GeneXpert® rapid TB test machines, in
1 c o u n t r i e s 2 0 1 3 .
https://www.who.int/news/item/11-06-2013-
largest-ever-roll-out-of-genexpert-rapid-tbtest-machines-in-21-countries
TB Facts.org. GeneXpert- testing for TB and
drug resistant TB.
United States Centers for Disease Control. TB
Diagnostic Tool: Xpert MTB/RIF Assay Fact
S h e e t . 2 0 1 6 .
https://www.cdc.gov/tb/publications/factsheet
s/testing/xpert_mtb-rif.htm
Harries AD, Kumar AMV. Challenges and
Progress with Diagnosing Pulmonary
Tuberculosis in Low- and Middle-Income
Countries. Diagnostics (Basel). 2018 ;8(4):78.
Dzodanu EG, Afrifa J, Acheampong DO,
Dadzie I. Diagnostic Yield of Fluorescence and
Ziehl-Neelsen Staining Techniques in the
Diagnosis of Pulmonary Tuberculosis: A
Comparative Study in a District Health
Facility. Tuberculosis Research and Treatment,
0 1 9 ; 4 0 9 1 9 3 7 : 1 - 6 .
https://doi.org/10.1155/2019/4091937
Chandra TJ, Selvaraj R, Sharma YV. Same day
sputum smear microscopy for the diagnosis of
pulmonary tuberculosis: Ziehl-Neelsen versus
fluorescent staining. J Family Med Prim Care.
0 1 5 ; 4 ( 4 ) : 5 2 5 - 8 .
https://doi.org/10.4103/2249-4863.174273
United States Centers for Disease Control.
Chapter 6 Treatment of Tuberculosis Disease -
C D C .
https://www.cdc.gov/tb/education/corecurr/pd
f/chapter6.pdf
Seung KJ, Keshavjee S, Rich ML. MultidrugResistant Tuberculosis and Extensively DrugResistant Tuberculosis. Cold Spring Harb
Pe rspe c t Med. 2015;5(9): a017863.
https://doi.org/10.1101/cshperspect.a017863 .
Tajbakhsh A, Ghasemi F, Mirbagheri SZ,
Momen Heravi M, Rezaee M, Meshkat Z.
Investigation of the rpoB Mutations Causing
Rifampin Resistance by Rapid Screening in
Mycobacterium Tuberculosis in North-East of
Iran. Iran J Pathol. 2018 Fall;13(4):429-437.
Tavanaee SA, Ashna H, Kaffash A, Khaledi A,
Ghazvini K. Mutations of rpob Gene
Associated with Rifampin Resistance among
Mycobacterium Tuberculosis Isolated in
Tuberculosis Regional Reference Laboratory
in Northeast of Iran during 2015-2016. Ethiop
J Health Sci. 2018 May;28(3):299-304.
https://doi.org/10.4314/ejhs.v28i3.7 .
Goldstein, B. Resistance to rifampicin: a
review. J Antibiot 67, 625–630 (2014).
https://doi.org/10.1038/ja.2014.107
Nusrath UA, Hassan S, Indira K V, Revathy R,
Hanna LE. Insights into RpoB clinical mutants
in mediating rifampicin resistance in
Mycobacterium tuberculosis. J Mol Graph
M o d e l . 2 0 1 6 ; 6 7 : 2 0 - 3 2 .
Otaigbe et al., 2024
Res. J. Health Sci. Vol 12(1), March 2024 48
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmgm.2016.04.005 .
Prasad R, Gupta N, Banka A. Multidrugresistant tuberculosis/rifampicin-resistant
tuberculosis: Principles of management. Lung
I n d i a . 2 0 1 8 J a n -Fe b ; 3 5 ( 1 ): 7 8 - 8 1 .
https://doi.org/10.4103/lungindia.lungindia_9
_17
Adejumo OA, Olusola-Faleye B, Adepoju V,
Bowale A, Adesola S, Falana A et al.
Prevalence of rifampicin resistant tuberculosis
and associated factors among presumptive
tuberculosis patients in a secondary referral
hospital in Lagos Nigeria. Afr Health Sci.
0 1 8 ; 1 8 ( 3 ) : 4 7 2 - 4 7 8 .
https://doi.org/10.4314/ahs.v18i3.2
Lu J, Li H, Dong F, Shi J, Yang H, Han S, et al.
The Feasibility of Xpert MTB/RIF Testing to
Detect Rifampicin Resistance among
Childhood Tuberculosis for Prevalence
Surveys in Northern China. Biomed Res Int.
0 1 7 ; 2 0 1 7 : 5 8 5 7 3 6 9 .
https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/5857369
Mulu W, Abera B, Yimer M,. et al. Rifampicinresistance pattern of Mycobacterium
tuberculosis and associated factors among
presumptive tuberculosis patients referred to
Debre Markos Referral Hospital, Ethiopia: a
cross-sectional study. BMC Res Notes.
;10:8 https://doi.org/10.1186/s13104-
-2328-4
Onyedum CC, Alobu I, Ukwaja KN.
Prevalence of drug-resistant tuberculosis in
Nigeria: A systematic review and metaanalysis. PLoS One. 2017;12(7):e0180996.
https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0180996
Munthali T, Chabala C, Chama E, Mugode R,
Kapata N, Musonda P, et al. Tuberculosis
caseload in children with severe acute
malnutrition related with high hospital-based
mortality in Lusaka, Zambia. BMC Res Notes.
0 1 7 ; 1 0 ( 1 ) : 2 0 6 .
https://doi.org/10.1186/s13104-017-2529-5
López-Varela E, Augusto OJ, Gondo K,
Garcia-Basterio AL, Fraile O, Ira T,et al.
Incidence of tuberculosis among young
children in rural Mozambique. Pediatr Infect
D i s J . 2 0 1 5 ; 3 4 ( 7 ) : 6 8 6 – 6 9 2 .
https://doi.org/10.1097/INF.00000000000007
Marais BJ, Obihara CC, Gie RP, Schaaf HS,
Hesseling AC, Lombard C et al. The
prevalence of symptoms associated with
pulmonary tuberculosis in randomly selected
children from a high burden community. Arch
Dis Child. 2005;90(11):1166–1170.
https://doi.org/10.1136/adc.2004.060640
Chipinduro M, Mateveke K, Makamure B,
Ferrand RA, Gomo E. Stool Xpert® MTB/RIF
test for the diagnosis of childhood pulmonary
tuberculosis at primary clinics in Zimbabwe.
Int J Tuberc Lung Dis. 2017;21(2):161–166.
https://doi.org/10.5588/ijtld.16.0357 .
Jaganath D, Zalwango S, Okware B, Nsereko
M, Kisingo H, Malone LS, et al. Contact
investigation for active tuberculosis among
child contacts in Uganda. Clin Infect Dis.
0 1 3 ; 5 7 ( 1 2 ) : 1 6 8 5 – 1 6 9 2 .
https://doi.org/10.1093/cid/cit645
Arega B, Menbere F, Getachew Y. Prevalence
of rifampicin resistant Mycobacterium
tuberculosis among presumptive tuberculosis
patients in selected governmental hospitals in
Addis Ababa, Ethiopia. BMC Infect Dis.
;19(1):307.30947695
Sultana AT, Gathia R, Huda MM, Begum JA,
Amin MR. Pattern of childhood tuberculosis
among the patients admitted in Dhaka Shishu
(Children) Hospital. Northern Int Med Coll J.
0 1 7 ; 8 ( 2 ) : 2 1 3 – 2 1 5 .
https://doi.org/10.3329/nimcj.v8i2.32552
Garba MA, Ogunbosi BO, Musa A, Ibraheem
RM, Alao MA, Jiya-Chitumu EN et al. Trends
in pediatric tuberculosis diagnosis utilizing
xpert Mycobacterium tuberculosis/Rifampicin
in a poor-resource, high-burden region: A
retrospective, multicenter study. Int J
M y c o b a c t e ri o l. 2 0 2 3 ; 1 2 ( 1 ): 7 7 - 8 1
https://doi.org/10.4103/ijmy.ijmy_1_23
Ogbudebe CL, Adepoju V, Ekerete-Udofia C,
Abu E, Egesemba G, Chukwueme N, et al.
Childhood Tuberculosis in Nigeria: Disease
Presentation and Treatment Outcomes. Health
S e r v I n s i g h t s . 2 0 1 8 ; 1 1 : 1 - 7 .
https://doi.org/10.1177/1178632918757490
Fadeyi A, Desalu OO, Ugwuoke C, Opanwa
OA, Nwabuisi C, Salami AK. Prevalence of
Rifampicin-Resistant Tuberculosis among
Patients Previously Treated for Pulmonary
Tuberculosis in North-Western, Nigeria. Niger
M e d J . 2 0 1 7 ; 5 8 ( 6 ) : 1 6 1 - 1 6 6 .
https://doi.org/10.4103/nmj.NMJ_41_17
Mathema B, Andrews JR, Cohen T, Borgdorff
MW, Behr M, Glynn JR, et al. Drivers of
Tuberculosis Transmission. J Infect Dis.
0 1 7 ; 2 1 6 ( s u p p l _ 6 ) : S 6 4 4 - S 6 5 3 .
https://doi.org/10.1093/infdis/jix354
Diel R, Nienhaus A. Pathways of TB
Transmission in Children-A Systematic
Review of Molecular Epidemiological
Studies. Int J Environ Res Public Health.
0 2 3 ; 2 0 ( 3 ) : 1 7 3 7 .
https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph20031737
Hesseling AC, Kim S, Madhi S, Nachman S,
Schaaf HS, Violari A et al. High prevalence of
drug resistance amongst HIV-exposed andinfected children in a tuberculosis prevention
trial. Int J Tuberculosis Lung Dis.
0 1 2 ; 1 6 ( 2 ) : 1 9 2 – 1 9 5 .
https://doi.org/10.5588/ijtld.10.0795
Jiao W, Liu Z, Han R, Zhao X, Dong F, Dong
H.et al. Prevalence of drug resistant
Otaigbe et al., 2024
Res. J. Health Sci. Vol 12(1), March 2024 49
Mycobacterium tuberculosis among children
in China. Tuberculosis. 2015;95(3):315–320.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tube.2015.02.041
Adisa R, Ayandokun TT, Ige OM. Knowledge
about tuberculosis, treatment adherence and
outcome among ambulatory patients with
drug-sensitive tuberculosis in two directlyobserved treatment centres in Southwest
Nigeria. BMC Public Health. 2021 ;21(1):677.
https://doi.org/10.1186/s12889-021-10698-9
Anochie PI, Onyeneke EC, Onyeozirila AC,
Igbolekwu LC, Onyeneke BC, Ogu AC.
Evaluation of public awareness and attitude to
pulmonary tuberculosis in a Nigerian rural
community. Germs. 2013;3(2):52-62.
https://doi.org/10.11599/germs.2013.1037
Roy P, Vekemans J, Clark A, Sanderson C,
Harris RC, White RG.Potential effect of age of
BCG vaccination on global paediatric
tuberculosis mortality: a modelling study.
Lancet Glob Health. 2019 Dec;7(12):e1655-
e1663. https://doi.org/10.1016/S2214-
X(19)30444-9
O'Riordan P, Schwab U, Logan S, Cooke G,
Wilkinson RJ, Davidson RN, Bassett P, Wall R,
Pasvol G, Flanagan KL. Rapid molecular
detection of rifampicin resistance facilitates
early diagnosis and treatment of multi-drug
resistant tuberculosis: case control study. PLoS
O n e . 2 0 0 8 ; 3 ( 9 ) : e 3 1 7 3 .
https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0003173
World Health Organization. Global research
agenda for antimicrobial resistance in human
h e a l t h . P o l i c y b r i e f . 2 0 2 3 .
https://cdn.who.int/media/docs/defaultsource/antimicrobial-resistance/amr-spcnpm/who-global-research-agenda-for-amr-inh u m a n - h e a l t h - - - p o l i c y -
brief.pdf?sfvrsn=f86aa073_4&download=tru
e
Moussa HSh, Bayoumi FS, Ali AM.
Evaluation of GeneXpert MTB/RIF assay for
direct diagnosis of pulmonary tuberculosis.
Saudi Med J. 2016;37(10):1076-81.
https://doi.org/10.15537/smj.2016.10.14998
Tropical Disease Research (TDR). Integrating
GeneXpert molecular testing technology in
national health systems – lessons from four
implementation research studies. 2022.
https://tdr.who.int/newsroom/news/item/17-
-2022-integrating-genexpert-moleculartesting-technology-in-national-healthsystems-lessons-from-four-implementationresearch-studies
Nalugwa T, Shete PB, Nantale M, Farr K, Ojok
C, Ochom E, et al.. Challenges with scale-up of
GeneXpert MTB/RIF® in Uganda: a health
systems perspective. BMC Health Serv Res.
0 2 0 ; 2 0 ( 1 ) : 1 6 2 .
https://doi.org/10.1186/s12913-020-4997-x .
Ramsay A, Harries AD. The clinical value of
new diagnostic tools for tuberculosis. F1000
M e d R e p . 2 0 0 9 ; 1 : 3 6 .
Pai, M., Dewan, P.K. & Swaminathan, S.
Transforming tuberculosis diagnosis. Nat
M i c r o b i o l 8 , 7 5 6 – 7 5 9 ( 2 0 2 3 ) .
https://doi.org/10.1038/s41564-023-01365-3
Shin SS, Seung KJ. Tuberculosis. In:Magill
AJ, Solomon T, Hill TR, Ryan ET, editors.
Hunter's Tropical Medicine and Emerging
Infectious Disease. 9th ed. London: Elsevier,
; p.416-432.
Dookie N, Khan A, Padayatchi N, Naidoo K.
Application of Next Generation Sequencing
for Diagnosis and Clinical Management of
Drug-Resistant Tuberculosis: Updates on
Recent Developments in the Field. Front
Microbiol. 2022 Mar 24;13:775030.
https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2022.775030
Hasan Z, Shakoor S, Hasan R. Importance of
next-generation diagnostics in control of
tuberculosis in LMICs. EBioMedicine.
0 2 1 ; 7 4 : 1 0 3 7 5 3 .
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Research Journal of Health Sciences

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
Research Journal of Health Sciences journal is a peer reviewed, Open Access journal. The Journal subscribed to terms and conditions of Open Access publication. Articles are distributed under the terms of Creative Commons License (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0). (http://creativecommons.org/licences/by-nc-nd/4.0). All articles are made freely accessible for everyone to read, download, copy and distribute as long as appropriate credit is given and the new creations are licensed under the identical terms.

