Effect of psychoactive substance use on academic activities and performance among undergraduates of University of Lagos
Keywords:
Psychoactive substance, academic performance, undergraduate studentsAbstract
Background: The objective of this study was to assess the effect of psychoactive substance use on academic performance among university students of Lagos undergraduates.
Methods: This is a descriptive cross-sectional study to assess psychoactive substance use and its relation to academic performance among undergraduate students of the University of Lagos. A multi-stage sampling technique was used to select the participants. Data was collected using a self-administered semistructured questionnaire adapted from WHO model core questionnaire self-administered format. Data was collected and analyzed using the free-liscence software package Epi-Info, version 7.2.2.16. Chi square and Fisher's exact were used to test for any significant association between psychoactive substances use and academic performance of the respondents. Level of significance (p) was set at 0.05.
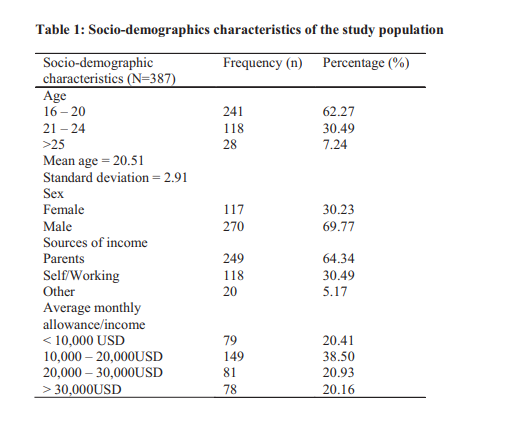
Result. Prevalence of psychoactive substance use was 28.6%. Male and female respondents were270 (69.77%) and 117(30.23%) respectively, with age range between 14 and 30 and mean age of 20.51 (SD)(±2.91) year. Alcohol was the most abused substance with 68.99%, this was followed by cigarette with 20.67% ever use prevalence. The mean age of first use of psychoactive substance was 16.31±3.89. Using the Grade Point Average system from the previous semester, majority of the respondents (87.08%) had GPA >2.50. Both frequency of studying and mean CGPA was statistically better among non-life time users and non-current users of alcohol, tobacco and cannabis in the male group. However there was no statical significance among female group. Using fischer exact test to assess the effect of age of fisrt substance use and mean CGPA. The age of first substance use was statistically significant for tobacco p = 0.007
Conclusion. Psychoactive substance use among students was common and negatively associated with students's academic performance especially among male gender.
References
M. Osain and V. Alekseevic. The effect of alcohol use on academic performance of university s t u d e n t s . A n n a l s o f G e n e r a l Psychiatry(2010);(9):215.
A. I. Balsa, L. M. Giuliano, and M. T. French. The effects of alcohol use on academic achievement in high school. Economics of Education Review(2011);(30):1–15,
G. T. Aklog and T. T. Girmay. Assessment of substance abuse and associated factors among students of debre markos poly technique college in debre markos town, East Gojjam Zone, Amhara Regional State, Ethiopia. Global Journal of Medical Research (2013);(13) 22-30
W. Deressa and A. Azazh. Substance use and its predictors among undergraduate medical students of Addis Ababa University in Ethiopia. BMC Public Health(2011);(11): 660-666 .
A. B. Makanjuola, T. O. Daramola, and A. O. Obembe.Psychoactive substance use among medical students in a Nigerian university. World Psychiatry(2007); ( 6): 112–114.
F. Venturelli, A. Poscia, G. Carrozzi, L. Sampaolo, A. Bargellini, and W. Ricciardi., Magnavita N. Prevalence of alcohol abuse among workers in Italy. La Medicina Del Lavoro(2017); (108) :52–63,
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention 2011. Control CfD, Prevention, others: Alcohol and other drug use and academic achievement. Atlanta, GA.
R. G. Cox, L. Zhang, W. D. Johnson, and D. R. Bender. Academic performance and substance use: findings from a state survey of public high school students. Journal of School Health (2007) ; (77) :109–115.
Meressa, A. Mossie, and Y. Gelaw. Effect of substance use on academic achievement of health officer and medical students of Jimma University, Southwest Ethiopia. Ethiopian Journal of Health sciences (2009); (19):155–163.
L. Atwoli, P. A. Mungla, M. N. Ndung'u, K. C. Kinoti, and E. M. Ogot. Prevalence of substance use among college students in Eldoret, western Kenya. BMC Psychiatry (2011); (11):34-42
C. Bakar, D. Gündogar, H. I. Ozisik Karaman, and I. Maral. Prevalence and related risk factors of tobacco, alcohol and illicit substance use among university students. European Journal of Psychiatry(2013);( 27):, 97–110.
A. Sahraian, M. Sharifian, B. Omidvar, and A. Javadpour. Prevalence of substance abuse among the medical students in southern Iran. Shiraz E Medical Journal (2010); (11):198–202.
M. S. van Heerden, A. T. Grimsrud, S. Seedat, L. Myer, D. R. Williams, and D. J. Stein, “Patterns of substance use in South Africa: results from the South African Stress and Health study,” South African Medical Journal, vol. 99, no. 5, pp. 358–366, 2009.
WHO ASSIST Working Group.The Alcohol, smoking and substance involvement screening test (ASSIST): development, reliability and feasibility. Addiction (2002); (97):1183–1194.
R. Humeniuk, R. Ali, T. F. Babor et al. Validation of the alcohol, smoking and substance involvement screening test (ASSIST). Addiction(2008);(103):1039–1047.
G. Tesfaye, A. Derese, and M. T. Hambisa. Substance use and associated factors among
University Students in Ethiopia: a CrossSectional Study. Journal of Addiction(2014); (2014):969837.
L. Samuel and M. T. Angamo. Substance use and sexual risk behavior and factors associated with HIV transmission in southern Ethiopia. IJPSR (2012); (3):1080–1086.
M. Gebreslassie, A. Feleke, and T. Melese. Psychoactive substances use and associated factors among Axum University students, Axum Town, North Ethiopia. BMC Public Health (2013);(13): 693 -699
A. M. Dhanookdhary, A. M. Gomez, R. Khan et al..Substance use among university students at the St augustine campus of the University of the
West Indies. West Indian Medical
Journal(2010);(59):641–649.
S B Aremu, Drug factors influencing its use among undergraduate students of A tertiary institution in Nigeria. Advances in Social Sciences Research Journal(2018);(5):388–97.
F.Adeyemo, B,Ohaeri,P U Okpala ,O Oghale. Prevalence of drug abuse amongst university students in Benin City, Nigeria. Public Health Research (2016);(6):31–7.
U H Ihezue. Drug abuse among medical students at a Nigerian university: Part 1. Prevalence and pattern of use. J Natl Med Assoc.
(1988);(80):81–5.
A. A. Reda, A. Moges, B. Yazew, and S. Biadgilign. Determinants of cigarette smoking among school adolescents in eastern Ethiopia: a cross-sectional study. Harm Reduction
Journal(2012);(9):39- 47
A. Poscia, P. Parente, E. M. Frisicale, A. A. Teleman, C. De Waure, and M. L. Di Pietro. Risky behaviours among university students in Italy. Annali dell'Istituto Superiore di Sanita(2015); (51): 111–115.
T. Damena, A. Mossie, and M. Tesfaye. Khat chewing and mental distress: a Community based study, in Jimma city, Southwestern Ethiopia. Ethiopian Journal of Health Sciences(2011); (21):37–45.
S. Mancevska, L. Bozinovska, J. Tecce, J.
Pluncevik-Gligoroska, and E. SivevskaSmilevska. Depression, anxiety and substance use in medical students in the Republic of
M a c e d o n i a . B r a t i s l a v a M e d i c a l
Journal(2008);(109):568–572.
Y. Dessie, J. Ebrahim, and T. Awoke. Mental distress among university students in Ethiopia: A cross sectional survey. Pan African Medical Journal (2013);(15):95-102
H W Yusuf, M K , S Zayyanu , and I I Umar . Prevalence and Impacts of Psychoactive Substance Abuse amongst Undergraduate University Students in Katsina State, Nigeria. Addict Health. (2021); (13): 221–231.
L. A. Tsvetkova and N. A. Antonova. The prevalence of drug use among university students in St. Petersburg, Russia. Psychology in Russia: State of the Art(2013);(1): 86–94
B. O. Abdu-Raheem. Sociological Factors To Drug Abuse And The Effects On Secondary School Students Academic Performance In Ekiti And Ondo States, Nigeria. Contemporary Issues in Education Research (2013); (6):233- 241
E. Gebrehanna, Y. Berhane, and A. Worku. Khat chewing among Ethiopian University Students—a growing concern. BMC Public
Health (2014);(14):1198-1210
R. M. Al-Sanosy. Pattern of khat abuse and academic performance among secondary school and college students in jazan region, kingdom of saudi arabia. Journal of Family and Community Medicine (2009);(16): 89–95.
B. Tilahun, A. Gedefaw, and A. Asefa. Predictors of self-reported academic performance among undergraduate medical students of Hawassa University, Ethiopia. Advances in Medical Education and Practice (2015):( 6): 305–315.
W. El Ansari, C. Stock, and C. Mills. Is Alcohol Consumption Associated with Poor Academic
Achievement in University Students?
International Journal of Preventive Medicine (2013);(4)1175–1188.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2023 Research Journal of Health Sciences

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
Research Journal of Health Sciences journal is a peer reviewed, Open Access journal. The Journal subscribed to terms and conditions of Open Access publication. Articles are distributed under the terms of Creative Commons License (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0). (http://creativecommons.org/licences/by-nc-nd/4.0). All articles are made freely accessible for everyone to read, download, copy and distribute as long as appropriate credit is given and the new creations are licensed under the identical terms.

