Assessment of health-related quality of life and its determinants among patients with diabetic foot ulcer in Ilorin, Nigeria
Keywords:
Diabetic Foot Ulcer, quality of Life, determinants, NigeriansAbstract
Background: The impact of foot ulceration on the psychosocial wellbeing of the Nigerian diabetic patients has not received enough attention. This study therefore attempted to evaluate the effect of diabetic foot ulcer on the quality of life of adults in a Nigerian diabetic population.
Methodology: The impacts of diabetic foot ulcer (DFU) on the quality of life (QoL) of 104 adults living with diabetes were assessed using The Diabetes Foot Ulcer Scale and their determinants.
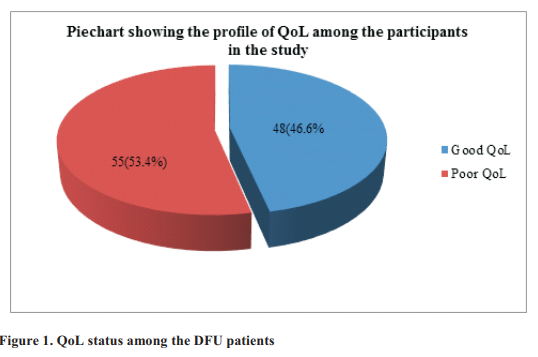
Results: The mean QoL score was 42.25. Fifty-five (53.4%) had poor QoL status while 48 (46.6%) had good QoL. Determinants of poor QoL outcome include low socio-economic status (p = 0.017), lack of a tertiary education (p= 0.027), no diabetes-education (p = < 0.001), low socioeconomic status (p = 0.017), multiple ulcers (p = 0.022) and Wagner grade >3 ulcers (p = 0.004).
Conclusion: Majority of patients with DFU in UITH, Nigeria have poor QoL and most of the predictors of poor QoL outcome are preventable and modifiable.
References
Boulton A J M. The diabetic foot: grand overview, epidemiology and pathogenesis. Diabetes Metab Res Rev 2008;24(Suppl 1):S3S6.
Gupta S K, Panda S and Singh S K. The etiopathogenesis of the diabetic foot: an unrelenting epidemic. International Journal of Lower Extremity Wounds 2010; 9(3):127– 131.
Pandsey S. Epidemiological aspects of Diabetic Foot. Int J Diab Dev Countries 1994;14:37-38.
Ogbera OA, Eregie O, Edo A and Ekpebegh C. Common clinical features of Diabetic Foot Ulcers: Perspectives from a Developing Nation. The International Journal of Lower Extremity Wounds 2008;7(2):93-98.
Frykberg RG, Zgonis T, Armstrong DG, Driver VR, Giurini JM, Kravitz SR et al. Diabetic Foot
Disorders: A Clinical Practice Guideline (2006 Revision). The Journal of Foot and Ankle Surgery 2006;45(5):S1-S66.
Reiber GE, Boyko EJ, Smith DG. Lower extremity foot ulcers and amputations in diabetes. In: Diabetes in America, 2nd ed, pp 409-427 , edited by MI Harris, C Cowie, and MP Stern, NIH Publication No. 95-1468; 1995.
Viswanathan V. Epidemiology of Diabetic Foot and Management of Foot Problems in India. The International Journal of Lower Extremity Wounds 2010; 9(3) 122–126.
Abetz L, Sutton M, Brady L, McNulty P and Gagnon D. D. The Diabetic Foot Ulcer Scale (DFS): a quality of life instrument for use in clinical trials. Practical Diabetes Int 2002: 19(6); 167-175.
Most RS, Sinnock P. The epidemiology of lower extremity amputation in diabetic individuals. Diabetes Care 1983; 6: 87-91.
Issa B A, Yusuff A D, Baiyewu O. The
Association between Psychiatric Disorders and Quality of Life of Patient with Diabetes Mellitus. Iran J Psychiatry 2007; 2: 30-34.
Ikem RT, Ikem IC, Ola BA. Relationship between depression, cognitive function and quality of life of Nigerians with diabetic foot ulcers, a preliminary controlled study. Acta Endocrinologica. 2009 Jan 1;5(1):75-83.
Habibu RA, Uloko AE, Gezawa ID, Ramalan MA, Muhammad FY, Abubakar UI, Muhammad
A. Health-related quality of life of persons with diabetic foot ulcers in a cosmopolitan city in northwestern Nigeria. Annals of African Medicine. 2022 Jul 1;21(3):250.
Ogunmodede A J, Abiodun O, Makanjuola A B, Olarinoye J K, Ogunmodede J A, Buhari O I. Burden of Care and Psychological Distress in Primary Caregivers of Patients with Type -2 Diabetes Mellitus in A Tertiary Hospital in Nigeria. Ethiop J Health Sci. 2019;29(6):697.
Alrub AA, Hyassat D, Khader YS, Bani-Mustafa R, Younes N, Ajlouni K. Factors associated with health-related quality of life among Jordanian patients with diabetic foot ulcer. Journal of diabetes research. 2019 Jan 17;2019.
Amira Abbassi, Asma Ben Hassine, Asma Ben Cheikh and Nabiha Boufia. Quality of life in patients with diabetic foot ulcers in Tunisia. Wound Middle East 2019;6,2:36-42.
WG Meijer, J. Trip, SMHJ Jaegers, TP Links, AJ Smits, JW Groothoff, WH Eisma J. Quality of life in patients with diabetic foot ulcers. Disability and rehabilitation. 2001 Jan 1;23(8):336-40.
Gilpin H, Lagan K. Quality of life aspects associated with diabetic foot ulcers: A review. The Diabetic Foot Journal. 2008;11(2):56-62.
Ahmad A, Abujbara M, Jaddou H, Younes NA, Ajlouni K. Anxiety and depression among adult patients with diabetic foot: prevalence and associated factors. Journal of clinical medicine research. 2018 May;10(5):411.
Raghav A, Khan ZA, Labala RK, Ahmad J, Noor S, Mishra BK. Financial burden of diabetic foot ulcers to world: a progressive topic to discuss always. Therapeutic advances in endocrinology and metabolism. 2018 Jan;9(1):29-31.
Powdthavee N, Lekfuangfu WN, Wooden M. What's the good of education on our overall quality of life? A simultaneous equation model of education and life satisfaction for Australia. Journal of behavioral and experimental economics. 2015 Feb 1;54:10-21.
Sekhar MS, Unnikrishnan MK, Vijayanarayana K, Rodrigues GS. Impact of patient-education on health related quality of life of diabetic foot ulcer patients: A randomized study. Clinical Epidemiology and Global Health. 2019 Sep 1;7(3):382-8.
Apelqvist J, Agardh CD, Castenfors J, Larsson J, Stenström A. Wound classification is more important than site of ulceration in the outcome of diabetic foot ulcers. Diabetic medicine. 1989 Aug;6(6):526-30.
Polikandrioti M. Quality of life in diabetic foot ulcer, grade 3: associated demographic factors. Folia Medica. 2022 Apr 30;64(2):229-39.
Valensi P, Girod I, Baron F, et al. Quality of life and clinical correlates in patients with diabetic foot ulcers. Diabetes Metab 2005; 31(3 Pt
:263–71
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2023 Research Journal of Health Sciences

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
Research Journal of Health Sciences journal is a peer reviewed, Open Access journal. The Journal subscribed to terms and conditions of Open Access publication. Articles are distributed under the terms of Creative Commons License (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0). (http://creativecommons.org/licences/by-nc-nd/4.0). All articles are made freely accessible for everyone to read, download, copy and distribute as long as appropriate credit is given and the new creations are licensed under the identical terms.

