Management of type B2 and B3 post-operative proximal periprosthetic femoral fractures, Oghara experience.
Keywords:
Periprosthetic femoral fracture, Long stem hip prosthesis, Vancouver classification, osteolysisAbstract
Objective: To report the outcome of treatment of Types B2 and B3 Post- operative Periprosthetic proximal femoral fracture (PPFF) in four patients treated in Delta State University Teaching Hospital, Oghara, Delta State, using Vancouver classification of Duncan and Masri.
Methodology: A retrospective study of four cases managed in this hospital. Information retrieved from case notes were sex, age, duration of prosthesis, treatment given, complications and outcome of treatment.
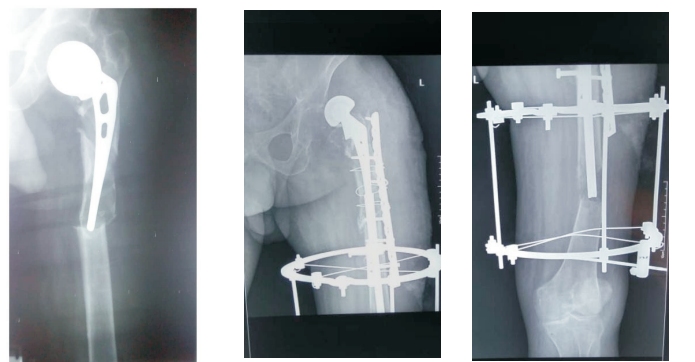
Result: A total of 4 patients were reviewed in the study, 2 males and 2 females with a M: F of 1: 1. Duration of the implant before treatment was 5-12 years (mean of 8.3years). Age range was 60-83years (mean of 67.5 years). Two patients had Type B2 and two had Type B3. Average intraoperative blood loss was 1 litre. Duration of surgery was 3-4 hours. Duration of hospital stay was between 3 weeks and 5 months. The complications seen were primary haemorrhage, wound infection, hip dislocation and pulmonary embolism. The outcome was good for 3 patients and fair in 1, using Harris Hip Score.
Conclusion: Vancouver classification of Duncan and Masri is effective in the treatment of PPFF.
References
Marsland D, Mears S.C. A Review of
Periprosthetic femoral Fractures Associated with Total Hip Arthroplasty. Geriatric Orthop. Surg. Rehabil. 2012;3(3):107-120
Berry DJ. Periprosthetic fractures associated with osteolysis: a problem on the rise. J Arthroplasty. 2003;18(3 suppl 1):107–111
Lindahl H, Malchau H, Herberts P, Garellick G. Periprosthetic femoral fractures: classification and demographics of 1049 periprosthetic femoral fractures from the Swedish National Hip Arthroplasty Register. J Arthroplasty.
;20(7):857–865
Lindahl H, Garellick G, Regner H, Herberts P, Malchau H. Three hundred and twenty-one periprosthetic femoral fractures. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2006;88(6):1215–1222
Adolphson P, Jonsson U, Kalen R. Fractures of the ipsilateral femur after total hip arthroplasty. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 1987;106(6):353–357
Duncan CP, Masri BA. Fractures of the femur after hip replacement. Instr Course Lect. 1995;
:293–304
Duncan CP, Haddad FS. The Unified
Classification system (UCS): improving our understanding of periprosthetic fractures. Bone Joint J., 2014;96-B:713–716.
Rayan F, Dodd M, Haddad FS. European validation of the Vancouver classification of periprosthetic proximal femoral fractures. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2008;90(12):1576–1579
Franklin J, Malchau H. Risk factors for periprosthetic femoral fracture. Injury.
;38(6):655–660
Chakravarthy J, Bansal R, Cooper J. Locking plate osteosynthesis for Vancouver Type B1 and Type C periprosthetic fractures of femur: a report on 12 patients. Injury. 2007;38(6):725–733
Delasotta LA, Orozco F, Miller AG, Post Z, Ong A. Distal femoral fracture during primary total knee arthroplasty. J Orthop Surg (Hong Kong) 2015 Aug;23(2):202–204.
Serocki JH, Chandler RW, Dorr LD. Treatment of fractures about hip prostheses with compression plating. J Arthroplasty. 1992;7(2):129–135
Corten K, Vanrykel F, Bellemans J, Frederix PR, Simon JP, Broos PL. An algorithm for the surgical treatment of periprosthetic fractures of the femur around a well-fixed femoral component. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2009;91(11):1424–1430
Ricci WM, Bolhofner BR, Loftus T, Cox C,
Mitchell S, Borrelli J., Jr Indirect reduction and plate fixation, without grafting, for periprosthetic femoral shaft fractures about a stable intramedullary implant. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2005;87(10):2240–2245
Klein GR, Parvizi J, Rapuri V et al. Proximal Femoral Replacement for the treatment of Periprosthetic fracture. J Bone and Joint Surg. Am. 2005;87(8):1777-1781
Tsiridis E, Narvani AA, Haddad FS, Timperley JA, Gie GA. Impaction femoral allografting and cemented revision for periprosthetic femoral fractures. J Bone Joint Surg Br.
;86(8):1124–1132
Chandler HP, Tigges RG. The role of allografts in the treatment of periprosthetic femoral fractures. Instr Course Lect. 1998; 47:257–264
Gallagher JC, Sai AJ. Vitamin D insufficiency, deficiency, and bone health. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2010;95(6):2630–2633
Zuurmond RG, van Wijhe W, van Raay JJ, Bulstra SK. High incidence of complications and poor clinical outcome in the operative treatment of periprosthetic femoral fractures: an analysis of 71 cases. Injury. 2010;41(6):629–633
Lindahl H, Oden A, Garellick G, Malchau H. The excess mortality due to periprosthetic femur fracture. A study from the Swedish national hip a r t h r o p l a s t y r e g i s t e r . B o n e .
;40(5):1294–1298
Drew JM, Griffin WL, Odum SM, et al.
Survivorship after periprosthetic femur fracture: factors affecting outcome. The Journal of Arthroplasty. 2016; 31:1283–1288.
Bhattacharyya T, Chang D, Meigs JB, et al. Mortality after periprosthetic fracture of the f e m u r. J B o n e J o i n t S u r g A m .
;89(12):2658–62.
Toogood PA, Vail TP. Periprosthetic Fractures. A Common Problem with a Disproportionately High Impact on Healthcare Resources. J Arthroplasty. 2015;30(10):1688–1691.
Enemudo RET, Odatuwa-Omagbemi DO,
Edomwonyi EO, Okeke MO. Management of
Neglected Posterior Hip Dislocation Using a Two-Stage Procedure. Nigerian Research Journal of Clinical Sciences. 2015;5(2):119125
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2023 Research Journal of Health Sciences

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
Research Journal of Health Sciences journal is a peer reviewed, Open Access journal. The Journal subscribed to terms and conditions of Open Access publication. Articles are distributed under the terms of Creative Commons License (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0). (http://creativecommons.org/licences/by-nc-nd/4.0). All articles are made freely accessible for everyone to read, download, copy and distribute as long as appropriate credit is given and the new creations are licensed under the identical terms.

