A survey of headache among nursing students in a Nigerian university
Keywords:
Prevalence, Headache, Nursing students & trigger factorsAbstract
Objectives: Headache is a common neurological disorder associated with a significant disease burden particularly among young people. Data on headache among undergraduate students in Nigeria are still scanty. The main objectives were to determine the 1-year prevalence of headache and headache subtypes among a cohort of nursing undergraduate students, to identify trigger factors and assess mode of treatment of acute attacks among the affected students.
Methods: This was a cross– sectional descriptive study carried out over a 2-month period from September to October 2011 among nursing students of the Ladoke Akintola University of Technology, Osogbo Nigeria, who had recurrent headaches (unrelated to febrile illness or any underlying disease) in the past one year. Data were collected using a self – administered questionnaire. Demographic variables, age of onset of headache, past medical, family and social histories were obtained.
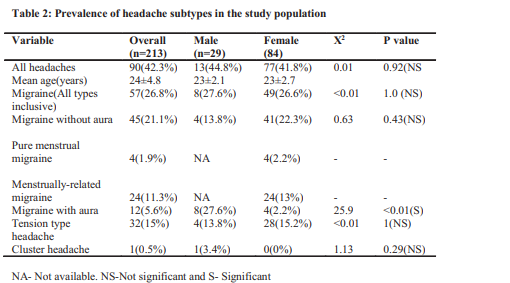
Results: A total of 213 out of 289 nursing students returned completed questionnaires giving a participation rate of 73.7%. Headache was reported by 90 students (42.3%) with higher prevalence in men (44.8%) compared to women (41.8%). Migraine headache was the commonest headache subtype constituting 26.8% .Common triggers of headache attacks included sleep deprivation (65.6%), physical and mental fatigue (53.3%). Only 8.9% of students affected by headache sought medical assistance during acute attack.
Conclusions: Our study found a relatively high proportion of migraine headache among nursing students with headache in this Nigerian University. Awareness of appropriate prophylactic and therapeutic medications was dismally low.
References
Global, regional, and national incidence, prevalence, and years lived with disability for 301 acute and chronic diseases and injuries in 188 countries, 1990-2013: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2013. Lancet 2015; 386:743-800
WHO. Headache Disorders. Factsheets Updated
April 2016 (Accessed 01 December 2016)
A v a i l a b l e a t
http://www.who.int/mediacentre/factsheets/fs27
/en/
Ojini FI, Okubadejo NU and Danesi MA. Prevalence and Clinical Characteristics of Headache in Medical Students of the University of Lagos, Nigeria. Cephalalgia2009 29: 472-477
Birru EM, Abay Z, Abdelwuhab M, Basazn A, Sirak B, Teni FS. Management of headache and associated factors among undergraduate medicine and health science students of University of Gondar, North West Ethiopia. The Journal of Headache and Pain 2016 17: 56 -63
Deleu D, Khan MA, Humaidan H, Al Mantheri Z, Al Hashami S Prevalence and clinical characteristics of headache in medical students in Oman. Headache 2001; 41: 798-804
Fendrich K, Vennemann M, Pfaffenrath V, Evers S, May A, Berger K, et al Headache prevalence among adolescents- the German DMKG headache study. Cephalalgia 2007;27: 347-354.
Tuzun,E.H, Eker L, Karaduman, A and Bayramoglu. M Prevalence and clinical characteristics of headache in university students in Turkey. The Pain Clinic. 2003; 15: 397-404.
Celik Y, Ekuklu G, Tokue B & Utku. Migraine prevalence and some related factors in Turkey. Headache 2005; 45:32-36.
Adoukonou T, Tognon-Tchegnonsi F, Kouna
P,Alabi A, Houinato D, Preux P.M. Prevalence of migraine among university students at Parakou, Benin: Across-sectional study. World Journal of Neuroscience.2014; 4:18-24
Ogunyemi A.O. Prevalence of Headache among Nigerian University Students.The Journal of Head and Face pain1984;24(3):127-130
Ofovwe G.E., Ofili AN. Prevalence and impact of headache and migraine among secondary school students in Nigeria. Headache. 2010 ;50 (10):1570-1575
Jyotika Basdav, et al. Impact of headaches on university students in Durban, South Africa. Springer plus. 2016; 5 (1): 1679-1684
Schoenberg B.S., Bolis C.L., Osuntokun B.O.,
Bademosi O, Adeuja AO, Nottidge VA , Olumide AO. Prevalence of headache and migrainous headache in Nigerian Africans: a communitybased study East Afr Med J 1992 (69): 196-199
Onwuekwe I, .Onyeka T, Aguwa E, EzealaAdikaibe B,. Ekenze O, Onuora O. Headache prevalence and its characterization amongst hospital workers in Enugu, South East Nigeria. Head Face Med. 2014; 10: 48-56
Oshinaike O, .Ojo O, Okubadejo N, Ojelabi O, and Dada A. Primary Headache Disorders at a Tertiary Health Facility in Lagos, Nigeria: Prevalence and Consultation Patterns. BioMed Research International. 2014 ;23
Headache Classification Committee of the International Headache Society (IHS). The
International Classification of Headache
Disorders, 3rd edition (Beta version);
Cephalalgia33 (9) 629–808
Falavigna A, Teles AR, Velho MC, Vedana VM, Da Silva RC; Mazzocchin T et al. Prevalence and impact of headache in undergraduate students in
S o u t h e r n B r a z i l . A r q . N e u r o -
Psiquiatr.2010;68(6):873-877
Ghorbani A, Abtahi SM, Fereidan-Esfahani M, Abtahi SH, Shemshaki H, Akbari M, MehrabiKoushki A. Prevalence and clinical characteristics of headache among medical students, Isfahan, Iran. J Res Med Sci. 2013;1 (1):24-27.
Zebenholzer K,Andree C,Lechner A, Broessner G, Lampl C, Luthringshausen G, et al. Prevalence, management and burden of episodic and chronic headaches—a cross-sectional multicentre study in eight Austrian headache centres. The Journal of Headache and Pain. 2015; 16:341-347
Stewart WF, Lipton RB, Liberman J. Variation in migraine prevalence by race. Neurology 1996; 47:52-59.
Loder E ,Tietjen GE ,Marcus DA. Evaluation and Management Issues in Migraine. Hospital
P h y s i c i a n 2 0 0 0 : 2 8 : 5 2 - 6 8 http://www.mayoclinic.com/health/migrainehea
dache/DS00120/DSECTION=risk-factors
(Accessed on December 1, 2015)
Sanvito WL, Monzillo PH, Peres MFP, Martinelli MO, Fera MP, Gouveia DA et al. The epidemiology of migraine in medical students. Headache 1996; 36:316-319
Susan Hutchinson. Prevention and management of menstrual migraine. Current Headache Reports 2007; 6:164-168
Mannix LK, Calhoun AH. Menstrual migraine. Curr Treat. Options Neurol 2004, 6:489-498 26. Lay CL, Mascellino AM. Menstrual Migraine: Diagnosis and treatment. Curr Pain Headache Rep 2001, 5:195-199
Rasmussen BK, Olesen J. Migraine with aura and migraine without aura: an epidemiological study. Cephalalgia 1992;12(4):221-228
Rasmussen et al. Epidemiology of headache in a general population: a prevalence study. J Clin Epidemiol 1991; 44(11): 1147-1157
Loretta Mueller. Tension Headache - the forgotten type of headache. Postgraduate Medicine 2002; 111(4): 25-44,49-50
Fischera M, Marziniak M, Gralow I, Evers S. The incidence and prevalence of cluster headache: a meta-analysis of population-based studies. Cephalalgia 2008 Jun; 28(6):614-618
D'Amico D, Solari A, Usai S, et al. for the Progetto Cefalee Lombardia Group.
Improvement in quality of life and activity limitations in migraine patients after prophylaxis. A prospective longitudinal multicenter study. Cephalalgia. 2006; 26: 691-696
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2023 Research Journal of Health Sciences

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
Research Journal of Health Sciences journal is a peer reviewed, Open Access journal. The Journal subscribed to terms and conditions of Open Access publication. Articles are distributed under the terms of Creative Commons License (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0). (http://creativecommons.org/licences/by-nc-nd/4.0). All articles are made freely accessible for everyone to read, download, copy and distribute as long as appropriate credit is given and the new creations are licensed under the identical terms.

