Comparison of the efficacy of atracurium pretreatment versus magnesium sulphate for prevention of suxamethonium-induced fasciculation and post-operative myalgia
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.4314/rejhs.v11i2.5Keywords:
Suxamethonium, Fasciculation, Myalgia, Atracurium, Magnesium SulphateAbstract
Background: Suxamethonium remains the best option for rapid sequence induction, it is the only depolarizing muscle relaxant in clinical use. However, fasciculation and myalgia are frequent adverse effects of the drug. Myalgia can last for several days with associated discomfort. Non-depolarizing muscle relaxant and magnesium sulphate have been tried as pretreatments to attenuate the fasciculation and myalgia with varying results.
Methods: A double blind, randomized study of 100 adult surgical patients of ASA I or II Class were recruited to receive either intravenous atracurium (0.05mg/kg) (Group A) or intravenous magnesium sulphate (30mg/kg)(Group B). The occurrence, severity and duration of fasciculation as well as the occurrence and severity of post-operative myalgia were also recorded.
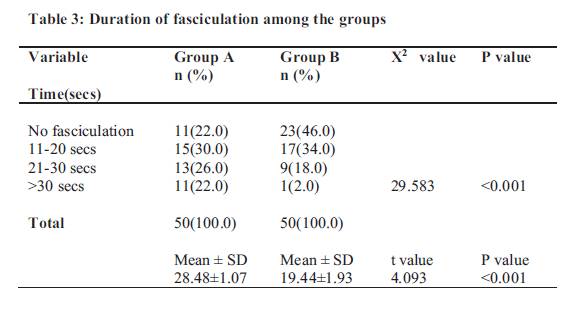
Results: Muscle fasciculation occurred in 39 (78%) patients in Group A and 27(54%) patients in Group B (p= 0.001). The severity of fasciculation was mild to moderate in Group B while Group A in addition also recorded some cases of severe episodes of fasciculation. Mean duration of fasciculation in Group A was
longer (28.48 ± 1.07sec) than in group B (19.44± 1.93seconds) (p= 0.001). Post-operative myalgia was not experienced at 6hrs and 48hrs, while 2 patients (1 in each Group) had it at 12hrs. At 24hrs, postoperative myalgia was present in 13(26%) patients in group A and 5(10%) patients in group B, (p=0.043). The severity of post-operative myalgia recorded both at 12hrs and 24hrs was mild.
Conclusion: Magnesium sulphate demonstrated better efficacy at reducing fasciculation and postoperative myalgia than atracurium
References
Chingmuh L, Ronald L.K. Clinical implications of new neuromuscular concepts and agents: so long, neostigmine! So long, sux! J Crit Care. 2009; 24(1):43-49.
Theroux MC, Rose JB, Lyengar S, Katz MS. Succinylcholine pretreatment using galamine or mivacurium during rapid sequence induction in children: a randomized, controlled study. J Clin Anaesth. 2001; 13(4):287-292
Raman SK, San WM. Fasciculations, myalgia a n d b i o c h emi c a l c h a n g e s f o l l owi n g succinylcholine with atracurium and lidocaine pretreatment. Can J Anaesth. 1997; 44:498-502.
Ursekar R, Kadam R, Aphale SS. Effect of magnesium sulphate on succinylcholine-induced fasciculation and post-operative myalgia. International Educational Scientific Research Journal 2016; 2 (4):13-14.
Stacey MR, Barclay K, Asai T, Vaughan RS. Ef f e c t s o f ma g n e s i um s u l p h a t e o n suxamethonium-induced complications during rapid sequence induction of anesthesia. Anesthesia 1995; 50(11):933-6.
Abdulatif M, Ahmed A, Mukhtar A, Badawy S. The effect of magnesium sulphate infusion on the incidence and severity of emergence agitation in children undergoing adenotonsillectomy using sevoflurane anesthesia. Anesthesia. 2013; 68(10): 1045-1052.
Srivastava VK, Agrawal S, Nimbhorkar VK, Mishra A, Sharma S, Panda PK. Prophylactic use of pregabalin for prevention of succinylcholine induced fasciculation and myalgia: a randomized, double-blinded, placebo-controlled study. Braz J Anesth. 2016; 66 (2):165-170.
Hassani M, Sahraian MA. Lidocaine or Diazepam can decrease fasciculation induced by succinylcholine during induction of anesthesia. Middle East J Anaesthesiol. 2006; 18 (5):929-931.
Nasseri K, Arvien S. Effects of low-dose ketamine on succinylcholine-induced postoperative myalgia in outpatient surgeries: a randomized, double-blind study. J Pain Res. 2016; 9:503-508.
Amornyotin S, Santawat U, Rachatamukayanant P, Nilsuwankosit P, Pipatnaraphong H. Can lidocaine reduce succinylcholine induced postoperative myalgia? J Med Assoc.Thai 2002; 85 (3):969-974.
Wood JB, Attwood EC, Wood BM, Dowling RM. Bradley F. Vitamin C and post-suxamethonium pains. Anesthesia 1977; 32(1):21-24.
Shrivastava OP, Chatterji S, Kachhawa S, Daga SR. Calcium gluconate pretreatment for prevention of succinylcholine-induced myalgia. Anesth Analg. 1983; 62(1):59-62.
Kahraman S, Ercan S, Aypar U, Erdem K. Effect of preoperative i.m. administration of diclofenac on suxamethonium-induced myalgia. Br J Anaesth. 1993; 71:238-241.
Schreiber JU, Lysakowski C, Fuchs-Buder T, Tramer MR. Prevention of succinylcholine induced fasciculation and myalgia: a metaanalysis of randomized trials. Anesthesiology 2005; 103(4):877-884.
Al-alami AA, Zestos MM, Baraka AS. Pediatric laryngospasm: prevention and treatment. Curr Opin Anaesthesiol 2009; 22(3): 388-95.
Famewo C.E. A study of different doses of atracurium to prevent suxamethonium-induced fasciculations. West Afr J Med. 1990; 9(3):214-219.
Pagani I, Ramaioli F, Albertario F, Mora R, Dionigi RV. Use of atracurium for the prevention of fasciculations and succinylcholine myalgia in athletes undergoing orthopedic surgery. Minerva Anestesiol 1990; 56(11):1413-1417.
Fatemeh H, Mojgan R. Comparism of atracurium and 'mini-dose' succinylcholine for preventing succinylcholine-induced muscle fasciculation. A randomized double blind, placebo- controlledstudy. Acta Anaesthesiol Taiwan 2010; 48:28-32.
Danladi KY, Sotunmbi PT, Eyelade OR. The effects of magnesium sulphate-pretreatment on suxamethonium-induced complications during induction of general endotracheal anesthesia. Afr J Med Sci. 2007; 36 (1):43-7.
Das KM, Yasmin R, Khatun US, Alam T, AKM A, Debnath H. Effects of pretreatment with magnesium sulphate on suxamethonium induced complications during induction of general anesthesia-A placebo controlled study. JBSA 2013; 26 (1):27-32.
Garg K, Luthra N, Sud S, Kaul TK, Namrata. Effect of repeat bolus dose of propofol on succinylcholine-induced fasciculations and myalgia. J Mahatma Gandhi Inst Med Sci 2014; 19:106-111.
Kumar M, Talwar N, Goyal R, Shukla U, Sethi AK. Effect of magnesium sulfate with propofol induction of anesthesia on succinylcholineinduced fasciculations and myalgia. J Anaesthesiol Clin. Pharmacol. 2012; 28(1):81–85.
Gray C, Vickers MH, Dyson RM, Reynolds CM, Berry MJ. Magnesium sulphate has sex specific, dose-dependent vasodilator effects on preterm placental vessels. Biol Sex Differ. 2015; 6:22.
Shorogi M, Zahedi H, Farahbakhsh F, Sheikhvatan M, Abbasi A. The effect of thiopentone on severity and duration of succinylcholine-induced fasciculation. Clin Neuropharmacol. 2009; 32 (2):94-96.
Mingus ML, Herlich A, Eisenkraft JB. Attenuation of suxamethonium myalgias. Effect of midazolam and vecuronium. Anesthesia.1990; 45 (10):834-837.
Schreiber JU, Mencke T, Biedler A, Fürst O, Kleinschmidt S, Buchinger H, Fuchs-Buder T. Postoperative myalgia after succinylcholine: no evidence for an inflammatory origin. Anesth Analg. 2003; 96:1640-1644.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2023 Research Journal of Health Sciences

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
Research Journal of Health Sciences journal is a peer reviewed, Open Access journal. The Journal subscribed to terms and conditions of Open Access publication. Articles are distributed under the terms of Creative Commons License (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0). (http://creativecommons.org/licences/by-nc-nd/4.0). All articles are made freely accessible for everyone to read, download, copy and distribute as long as appropriate credit is given and the new creations are licensed under the identical terms.





