Effects of vigabatrin, carbamazepine or its combination on the pituitarygonadal axis in male Wistar rats
Keywords:
epilepsy, vigabatrin, carbamazepine, sperm, testosteroneAbstract
Objectives: Epilepsy is the most common non-infectious neurologic disease in developing African countries following stroke and Alzheimer's disease. Most conventional antiepileptic drugs, due to their centrally acting potentials have been implicated in the deregulation of reproductive hormones. This study assessed the effect of the single and combined administration of vigabatrin (VIG) and carbamazepine (CBZ) on the pituitary-gonadal axis of male Wistar rats.
Methods: Fifty male Wistar rats were randomly divided into 5 groups (n=10). The animals were administered with distilled water (0.1 ml/kg/day), VIG (200 mg/kg/day), CBZ (200 mg/kg/day), VIGCBZ combination (100 mg/kg/day each) and VIG-CBZ combination (200 mg/kg/day each) for 8 weeks. Twenty-four hours after the last dose, 5 rats from each group were sacrificed, while the remaining 5 eventually sacrificed after another 8 week of drug withdrawal. The level of luteinizing hormone, follicle stimulating hormone and testosterone were determined from the serum. The weight of the reproductive organs and sperm indices were assayed, while the testicular tissue were examined for signs of histological alteration.
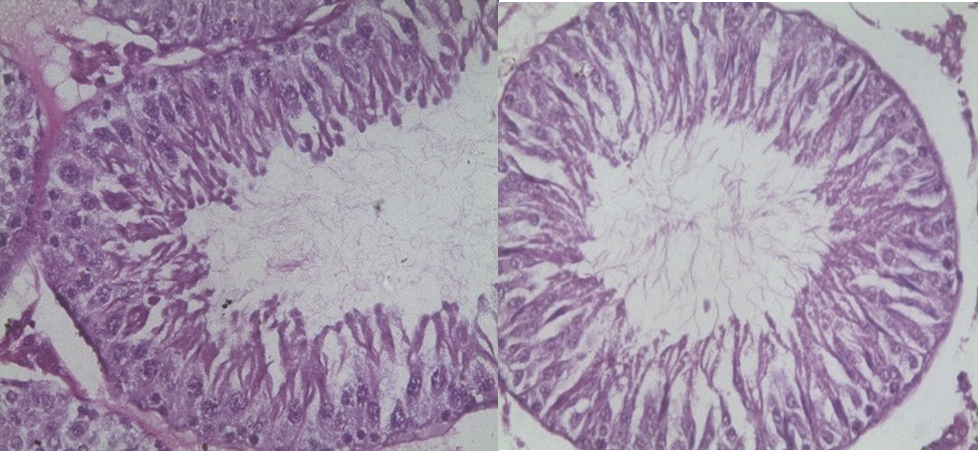
Results: The results showed significant decrease in the levels of luteinizing hormone, follicle stimulating hormone, testosterone and sperm physiological indices. Morphological alteration was noticed in the testes of all the treated rats. However, there was restoration of these parameters sequelae to 8 weeks cessation of treatment.
Conclusion: Single and combined administration of VIG and CBZ resulted into pituitary-gonadal axis hormonal deregulation and alterations in the sperm profile which were however reversible upon cessation of treatment.
References
Brodie, M.J., Elder A.T and Kwan P (2009). Epilepsy in later life. Lancet Neurology. 8:1019–1030.
Thurman, D. J., Beghi, E., Begley, C. E., Berg, A. T., Buchhalter, J. R., Ding, D., Hesdorffer, D. C., Hauser, W. A., Kazis, L., Kobau, R., Kroner, B., Labiner, D., Liow, K., Logroscino, G., Medina, M. T., Newton, C. R., Parko, K., Paschal, A., Preux, P. M., Sander, J. W., Selassie, A., Theodore, W., Tomson, T., Wiebe, S. and ILAE
C o m m i s s i o n o n , E p i d e m i o l o g y
(2011)."Standards for epidemiologic studies and surveillance of epilepsy." Epilepsia. 52 (7): 226232.
Eadie, M. J. (2012). "Shortcomings in the current treatment of epilepsy." Experimental Review of Neurotherapeutics12 (12):1419-1427.
Devlin, A., Odell, M., Charlton, J. and Koppel, S. (2012). "Epilepsy and driving: current status of research." Epilepsy research.102 (3): 135-152.
Brodie M.J., Elder A.T and Kwan P (2009). Epilepsy in later life. Lancet Neurology. 8:1019–1030.
Camfield P and Camfield C (2015). Incidence, prevalence and aetiology of seizures and epilepsy in children Epileptic Disorder 17 (2): 117-123.
Sander, J.W. (2004). The use of Antiepileptic Drugs – Principles and Practice. Epilepsia 45 (6): 1817 – 1829.
Kwan, P. and Brodie, M.J. (2006). Combination therapy in epilepsy: when and what to use. Drugs. 66 (14): 1817 – 1829.
Brodie, M.J. and Sills, G.J. (2011). Combining antiepileptic drugs – Rational Polytherapy. Seizure 20 (5): 369 – 375
Dana-Haeri, J., Oxley, J and Richens, A. (1982). Reduction of free testosterone by antiepileptic drugs. British Medical Journal284: 85-86.
Osuntokun, O.S, Olayiwola, G, Oladele A., Ola . . Iand AyokaAbiodun O(2017). Pathophysiology 24 (2):63-69.
Artama, M., Isojarvi, J. I. and Auvinen, A. (2006). Antiepileptic drug use and birth rate in patients with epilepsy--a population-based cohort study in Finland. Human Reproduction. 21(9): 2290-2293.
Shetty, A.J. and Narayana, K. (2007). The effect of carbamazepine on sperm morphology in Wistar rats. Indian Journal of Physiology and Pharmacology 51 (3): 255 – 260.
Sanchez-Alcaraz, A., Quintana, M.B., Lopez, E., Rodriguez, I and Llopis, P. (2002): Effect of vigabatrin on the pharmacokinetics of carbamazepine. Journal of clinical pharmacy and therapeutics 27 (6): 427 – 430.
Daoud A. S., Bataineh H., Otoom S. and AbdulZahra E. (2004). The effect of Vigabatrin, Lamotrigine and Gabapentin on the fertility, weights, sex hormones and biochemical profiles of male rats. Neuroendocrinology Letters 25(5):351-5.
Olaibi, K. O., Osuntokun, O. S. and
Omamuyovwi, M. I. (2014). Effects of chronic administration of gabapentin and carbamazepine on the histomorphology of the hippocampus and striatum. Annals of neuroscience. 21(2): 57-61.
Raji, Y., Ifabunmi, S. O., Akinsomisoye, O. S., Morakinyo, A. O. and Oloyo, A. K. (2005a). Gonadal responses to antipsychotic drugs; Chlorpromazine and Thioridazine reversibly suppress testicular functions in albino rats. International Journal of Pharmacology. 1 (3): 287-292.
Otoom, S., Batieneh, H., Hassan Z and Daoud A (2004). Effects of long- term use of Topiramate on fertility and growth parameter in adult Male Rats. Neuroendocrinology Letters 5 (25): 351355.
Maree, L., du-Plessis, S.S., Menkveld, R and van- der- Horst G (2010). Morphometric dimensions of the human sperm head depend on the staining method used. Human Reproduction 25 (6): 1369–1382.
Raji, Y., Udoh, U. S., Mowoyeka, O. O., Ononye, F. C. and Bolarinwa A. F. (2003). Implication of endocrine malfunction in male antifertility efficacy of Azadirachtaindica xtract in rats. African Journal of Medicine and Medical Science.32:159-165
Bito, V (2003). Effect of antiepileptic drugs on body weight. CNS drugs17 (11): 781–791.
Aydin, K., Serdaroglu, A. and Okuyaz, C. (2005). Serum insulin, leptin, and neuropeptide Y levels in epileptic children treated with valproate. Journal of Child Neurology. 20 (3): 848-851.
Sheth, R. D. and Montouris, G. (2008). Metabolic effects of AEDs: impact on body weight, lipids and glucose metabolism. International Review of Neurobiology. 83: 329-
Laxminarayana, B., Vijary, P. and Yeshwanth, R. (2010). Reproductive toxicity of sodium valproate in male rats. Indian Journal of pharmacology. 42 (2): 90 - 94
Meistrich, M. L. (1982). Quantitative correlation between testicular stem cell survival, sperm production and fertility in the mouse after treatment with different cytotoxic agents. Journal of Andrology. 3: 58 – 68.
Afaf, A. E. (2009). Influence of subchronic exposure of lead on biochemical markers and microelements in testicular tissue of rats. Nature and Science. 7 (2): 0740 -1545.
Da-Nian, Q. I. N. and Mary, A. L. (2001). Effect of testicular capsulotomy on fertility of rats. Asian Journal of Andrology. 3: 21 – 25.
Sharpe, R. M. (1994). Regulation of spermatogenesis. In. Knobil, E, Neil, J. D. The physiology of reproductive Raven Press, New York. Pp. 1363 – 1434
Vomberger, W., Prins, G., Musto, N. A. and Suarez- Quian, C. A. (1994). Andrology receptor distribution in the rat testis: New implications for androgen regulation of spermatogenesis. Endocrinology. 134: 2307 – 2316.
Ballester, J. M., Munoz, M. C., Dominguez, J., Rigau, T., Guinovart, J. J., Rodriguez-Gil, J. E. (2004).Insulin-dependent diabetes affects testicular functions by FSH and LH-linked mechanisns. Journal of Andrology. 25: 706-719.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2023 Research Journal of Health Sciences

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
Research Journal of Health Sciences journal is a peer reviewed, Open Access journal. The Journal subscribed to terms and conditions of Open Access publication. Articles are distributed under the terms of Creative Commons License (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0). (http://creativecommons.org/licences/by-nc-nd/4.0). All articles are made freely accessible for everyone to read, download, copy and distribute as long as appropriate credit is given and the new creations are licensed under the identical terms.

