Intradialysis stroke
Keywords:
Haemodialysis, Chronic kidney disease, Hypertension, atherosclerosisAbstract
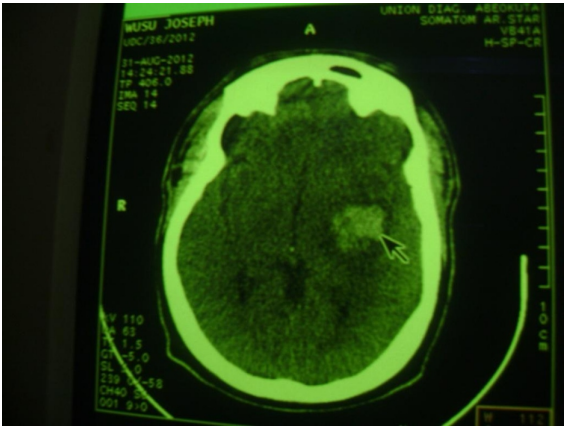
This case report showed an unusual complication arising from managing kidney failure patient. Haemodialysis procedure in most patients with kidney failure lowers their blood pressure. However, some patients exhibit paradoxical increase in BP during dialysis. There is considerably higher prevalence of clinical cardiovascular disease in the dialysis patients compared with the general population; this had been documented way back in 1974. Chronic kidney disease is associated with accelerated atherosclerosis, and high cardiovascular mortality in this group of patients may be attributed to this atherosclerosis. There is also vascular remodelling, which is characterized by: proportional increase in arterial diameter and wall thickness, this may be due to pressure overload which leads to wall hypertrophy and an increase in wall to lumen ratio or flow overload.
Ureamic vasculature predisposes dialysis patients to further injury by the presence of Framingham risk factors such as anaemia, inflammation, oxidative
stress, metabolic alterations, sympathetic over activity, electrolyte disturbances and vascular calcification, and thus predisposing them to stroke. Intra dialysis cardiovascular stroke is not common in this environment; we therefore presented a case of stroke during dialysis in a patient with chronic kidney disease.
References
Linder A, Charra B, Sherrard D.J, Schuibner B.H. Accelerated atherosclerosis in prolonged maintenance haemodialysis. N Engl. J Med. 1974;290: 697-701.
Vanholder R, Messy Z, Argiles A, Spasovski G, Verbeke F, Lamiere N. Chronic kidney disease as cause of cardiovascular morbidity and mortality. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2005; 20: 1048-1056.
Buzello M, Tornig J, Faulhaber J, Ehmke H, Ritz E, Amann K. The apolipoprotein e knock out mouse: a model documenting accelerated atherogenesis in uraemia. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2003; 14: 311-316.
Iseku K, Fukuyama K. Predictors of stroke in patients receiving chronic haemodialysis Kidney Int. 1996; 50: 1672-1675.
Parfrey P.S. Cardiac and Cerebrovascular diseases in chronic uraemia. Am J Kidney Dis. 1993; 21: 77-80.
Salako B.L. Managing chronic renal disease in Nigeria. Niger. Med J. 2001; 40(3) 75-77.
Kawamura M, Fijimoto S, Hisanga S, Yamamoto Y, Eto T. Incidence, outcome and risk factors of cerebrovascular events in patients undergoing maintenance heamodialysis. Am J Kidney Dis. 1998; 31: 991-996.
Abramson JL, Jurkovitz CT, Vaccarino V, Weintraub WS, McClellan W. Chronic kidney disease, anaemia and incident stroke in a middle aged community based population: The ARIC study. Kidney Int. 2003; 64: 610-615.
Seliger SL, Gillen DL, Longstreth WT, Kestenbaum B, Stehman-Breen CO. Elevated risk of stroke among patients with end stage renal disease. Kidney Int. 2003; 64: 603-9. 10. Ishida I, Hirakata H, Sugimori H, , Hirakata E, Ibayashi S, et al. Haemodialysis causes severe orthostatic reduction in cerebral blood flow velocity in diabetic patients. Am J. Kidney Dis. 1999; 34: 1096-104.
United States renal Data System: USRDS 2007 Annual Data Report. Bethesda, MD: The National Institutes of Digestive and Kidney Disease. 2007
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2023 Research Journal of Health Sciences

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
Research Journal of Health Sciences journal is a peer reviewed, Open Access journal. The Journal subscribed to terms and conditions of Open Access publication. Articles are distributed under the terms of Creative Commons License (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0). (http://creativecommons.org/licences/by-nc-nd/4.0). All articles are made freely accessible for everyone to read, download, copy and distribute as long as appropriate credit is given and the new creations are licensed under the identical terms.

