Obesity and hypoglycaemia in type 2 diabetes mellitus outpatients on insulin therapy in Nigeria–data from the multicentre evaluation of type 2 diabetes mellitus outpatients patients on insulin therapy (METOIN) study.
Abstract
Background and Objective: Despite the obvious benefits of early insulin use in
achieving good glycaemic control, insulin linked overweight/obesity and
hypoglycaemia are sources of concern and worry. Burden of these side effects among
type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) outpatients on insulin therapy in Nigeria is
unknown.
Subjects and Methods: This was a prospective, cross sectional and observational
study in which consenting T2DM outpatients that meet the inclusion criteria for the
study in five tertiary health facilities were simultaneously recruited and relevant data
obtained via investigator-administered questionnaire. Data obtained which included
gender, arthropometric measures, hypoglycaemia and where it was treated were
analyzed using Statistical Package for Social Sciences (SPSS) version 23.0 software.
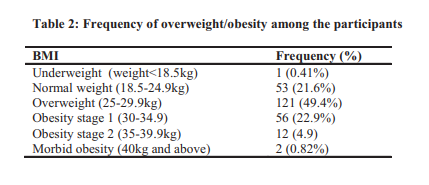
Results: A total of 245 T2DM outpatients were recruited into the study, made up of
107 (43.7%) male and 138 (56.3%) female. Of this, 121 (49.8%) patients were
overweight while 70 (28.7%) were obese. Among the patients, 104 (42.4%) T2DM
outpatients on insulin therapy reported hypoglycaemia which was mild in 83 (79.8%)
of the patients
Conclusion: A significant number of the type 2 DM outpatients on insulin therapy
were overweight/obese with mild hypoglycaemia in a majority of them.
References
Bonafede, M.M., Kalsekar, A., Pawaskar, M.
Ruiz MK, Torres AM et al. Insulin use and
persistence in patients with type 2 diabetes
adding mealtime insulin to a basal regimen: a
retrospective database analysis. BMC Endocr
D i s o r d 1 1 , 3 ( 2 0 1 1 ) .
https://doi.org/10.1186/1472-6823-11-3
, Koro CE, Bowlin SJ, Bourgeois N, Fedder DO.
Glycemic control from 1988 to 2000 among U.S.
adults diagnosed with type 2 diabetes: a
preliminary report. Diabetes Care. 2004
Jan;27(1):17-20. doi: 10.2337/diacare.27.1.17.
Nicasio J, Mcfarlane SI. Early insulin therapy
and the risks of cardiovascular disease in type 2
diabetes.Therapy.2005; 2(5): 685-688.
Meneghini L. Why and how to use insulin
therapy earlier in the management of type 2
diabetes. South Med J. 2007; 100(2): 164-174.
Ryan EA, Imes S, Wallace C. Short term
intensive insulin therapy in newly diagnosed type
diabetes. Diabetes care. 2004; 27(5): 1028-
Nichols GA, Koo YH, Shah SN. Delay of insulin
addition to oral combination therapy despite
inadequate glycaemic control: delay of insulin
therapy. J Gen Intern Med 2007; 22(4): 453-458.
Peyrot M, Rubin RR, Lauritzen T, Skovlund SE,
Snoek FJ, Matthews DR et al. Resistance to
insulin therapy among patients and providers:
results of the cross-national Diabetes Attitudes,
Wishes, and Needs (DAWN) study. Diabetes
Care. 2005 Nov;28(11):2673-9. doi:
2337/diacare.28.11.2673.
Caver C. Insulin treatment and the problem of
weight gain in type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Educ.
; 32(6): 910-917.
Hodism Israel, Insulin therapy, weight gain and
prognosis - A review. Diabetes, Obesity and
Metab, 2018 May: 20 (9); 2085-2092.
doi.org/10.1111/dom.13367
McCall AL. Insulin therapy and hypoglycaemia.
Endocrinol Metabol Clin North Am. 2012
March: 41(1); 57-87.
UK Prospective Diabetes Study Group. Effects of
Intensive blood glucose control with metformin
on complications in overweight patients with
type 2 diabetes (UKPDS 34) Lancet. 1998;
(9131): 854-865.
Cryer PE, Axelrod L, Grossman AB, Heller SR,
Montori VM, Seaquist ER et al. Evaluation and
management of adult hypoglycemic disorders: an
Endocrine Society Clinical Practice Guideline. J
Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2009 Mar;94(3):709-28.
doi: 10.1210/jc.2008-1410. .
Fadupin GT, Joseph EU, Keshinro OO.
Res. J. Health Sci. Vol 12(1), March 2024 4
Nkpozi et al., 2024
Prevalence of obesity in Nigeria: a case of
patients in Ibadan, Oyo state, Nigeria. Afr J Med
Med Sci 2004 Dec; 33(4): 381-384.
Gezawa ID, Uloko AE, Gwaram BA, Ibrahim
DA, Ugwu ET, Mohammed IY. Diabetes
Metabol Syndr Obes. 2019; 12: 2785-2790 doi:
2147/DMSO.S226054.
Ali YA, Almobarak AO, Awadalla H, Elmadhoun
WM, Ahmed MH. Obesity among Sudanese
adults with diabetes: a population based survey.
AnnTransl Med. 2017 Jun; 5(12): 252. doi:
2137/atm.2017.05.11
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Research Journal of Health Sciences

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
Research Journal of Health Sciences journal is a peer reviewed, Open Access journal. The Journal subscribed to terms and conditions of Open Access publication. Articles are distributed under the terms of Creative Commons License (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0). (http://creativecommons.org/licences/by-nc-nd/4.0). All articles are made freely accessible for everyone to read, download, copy and distribute as long as appropriate credit is given and the new creations are licensed under the identical terms.

