Determinants of quality of life of patients with uncomplicated diabetes mellitus attending endocrinology clinic, UNIOSUN Teaching Hospital, Osogbo, Osun State
Keywords:
Psychological experience, social-experience, quality of life, diabetes, patients, diabeticAbstract
Introduction: Diabetes Mellitus (DM) is a chronic metabolic disorder that poses significant problems to individuals living with it. The emotional anguish and psychological impact of DM on patients' quality of life (QoL) contribute to poor prognosis of the condition. Therefore, the goal of this study is to examine how psychological experiences and satisfaction with diabetic care affect patients' QoL.
Methods: A descriptive research survey conducted among one hundred and ten (110) diabetes patients attending the UNIOSUN Teaching Hospital's endocrinology clinic in Osun State, Nigeria between June and December, 2020. Modified Kessler psychological distress scale and World Health Organization Quality of Life Instrument (WHOQOL-BREF) were used to collect data. Data were analyzed using descriptive statistics of frequencies, percentages and tables, while inferential statistics of chi-square was used to test the stated hypothesis at 0.05 level of significance.
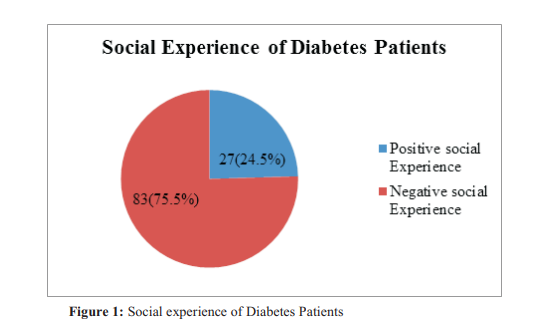
Results: The results showed that more than three-fourth of the patients had negative social 83(75.5%) and psychological 79 (71.8%) experiences with diabetic care, though majority 68(61.8%) demonstrated good quality of life. The result also showed a positive relationship between psychological experience and quality of life (x2=9.766; df=1; p-value=0.001) as well as social experiences and quality of life (x2=4.576; df=1; p-value=0.032). More so, socio-demographic characteristics of age, gender, marital status, level of education, occupation and income were significantly associated with quality of life of diabetes patients.
Conclusion: Overall quality of life of diabetes patients was observed to be good, although majority of diabetes patient had negative social and psychological experiences. Therefore, efforts to improve diabetic care must be intensified in clinical settings to promote good health outcomes and prevent negative social and psychological impact of diabetes mellitus.
References
Enang O, Omoronyia O, Asibong U, Ayuk A, Nwafor K, Legogie A. A case-control study of pattern and determinants of quality of life of patients with diabetes in a developing country.
Journal of the Egyptian Public Health
Association. 2021;96(1):1–11.
Koch M. Urbanisation, inequality, and noncommunicable disease risk. The Lancet Diabetes & Endocrinology. 2017;5(5):313.
Nwatu C, Onyekonwu C, Unaogu N, Ijeoma U, Onyeka T, Onwuekwe I, et al. Health related quality of life in nigerians with complicated diabetes mellitus–a study from Enugu, South East Nigeria. Nigerian Journal of Medicine. 2019;28(2):138–47.
Ogurtsova K, da Rocha Fernandes J, Huang Y, Linnenkamp U, Guariguata L, Cho NH, et al. IDF Diabetes Atlas: Global estimates for the prevalence of diabetes for 2015 and 2040. Diabetes research and clinical practice. 2017;128:40–50.
Rodríguez-Almagro J, García-Manzanares Á, Lucendo AJ, Hernández-Martínez A. Healthrelated quality of life in diabetes mellitus and its social, demographic and clinical determinants: A nationwide cross-sectional survey. Journal of Clinical Nursing [Internet]. 2018 Nov 1 [cited 2021 Aug 26];27(21–22):4212–23. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1111/jocn.14624
International Diabetes Federation. IDF Diabetes Atlas [Internet]. 9th Edition. Brussels, Belgium;
0 1 9 . A v a i l a b l e f r o m :
Adeleye J. The hazardous terrain of Diabetes mellitus in Nigeria: The time for action is now.
Research Journal of Health Sciences.
;9(1):69–76.
Sikdar KC, Wang PP, MacDonald D, Gadag VG. Diabetes and its impact on health-related quality of life: a life table analysis. Quality of Life Research. 2010;19(6):781–7.
Fernandez V. How to Code Complications: Healthcare Business Management Association Billing [Internet]. HBMA News. 2016 [cited 2022
F e b 6 ] . A v a i l a b l e f r o m :
https://www.hbma.org/news/public-
news/n_how-to-code-complications#
Papatheodorou K, Banach M, Bekiari E, Rizzo M, Edmonds M. Complications of diabetes 2017. Journal of diabetes research. 2018 Mar 11;2018.
Wukich DK, Joseph A, Ryan M, Ramirez C,
Irrgang JJ. Outcomes of ankle fractures in patients with uncomplicated versus complicated diabetes. Foot & Ankle International. 2011;32(2):120–30.
Wukich DK, Raspovic KM. Assessing healthrelated quality of life in patients with diabetic foot disease: why is it important and how can we improve? The 2017 Roger E. Pecoraro award lecture. Diabetes Care. 2018;41(3):391–7.
Chew BH, Mohd-Sidik S, Shariff-Ghazali S. Negative effects of diabetes–related distress on health-related quality of life: an evaluation among the adult patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus in three primary healthcare clinics in Malaysia. Health and Quality of Life Outcomes [Internet]. 2015 Nov 24;13(1):187. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1186/s12955-015-0384-4
Adu MD, Malabu UH, Malau-Aduli AE, MalauAduli BS. Enablers and barriers to effective diabetes self-management: A multi-national investigation. PloS one. 2019;14(6):e0217771.
Ruževièius J. Quality of Life and of Working Life: Conceptions and research. In17th Toulon-Verona International Conference, Liverpool John Moores University, England 2014 May (pp. 28-29).
Jannoo Z, Wah YB, Lazim AM, Hassali MA. Examining diabetes distress, medication
adherence, diabetes self-care activities, diabetesspecific quality of life and health-related quality of life among type 2 diabetes mellitus patients.
Journal of Clinical & Translational
Endocrinology [Internet]. 2017;9:48–54.
A v a i l a b l e f r o m : https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pi i/S2214623717300108
Bowen PG, Clay OJ, Lee LT, Vice J, Ovalle F, Crowe M. Associations of social support and selfefficacy with quality of life in older adults with diabetes. Journal of gerontological nursing. 2015;41(12):21–9.
Van Wilder L, Clays E, Devleesschauwer B, Pype P, Boeckxstaens P, Schrans D, et al. Health-related quality of life in patients with non-communicable disease: study protocol of a cross-sectional survey. BMJ open. 2020;10(9):e037131.
Gebremariam GT, Biratu S, Alemayehu M, Welie AG, Beyene K, Sander B, et al. Health-related quality of life of patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus at a tertiary care hospital in Ethiopia. PloS one. 2022;17(2):e0264199.
Abedini MR, Bijari B, Miri Z, ShakhsEmampour F, Abbasi A. The quality of life of the patients with diabetes type 2 using EQ-5D-5 L in Birjand.
Health and Quality of Life Outcomes.
;18(1):1–9.
World Health Organization. WHOQOL-BREF: introduction, administration, scoring and generic version of the assessment: field trial version, December 1996. World Health Organization; 1996.
Funnell MM, Bootle S, Stuckey HL. The diabetes attitudes, wishes and needs second study. Clinical Diabetes. 2015;33(1):32–6.
Pedron S, Emmert-Fees K, Laxy M, Schwettmann L. The impact of diabetes on labour market participation: a systematic review of results and methods. BMC Public Health. 2019;19(1):1–13.
Seuring T, Goryakin Y, Suhrcke M. The impact of diabetes on employment in Mexico. Economics & Human Biology. 2015;18:85–100.
Bhagavathula AS, Gebreyohannes EA, Abegaz TM, Abebe TB. Perceived obstacles faced by diabetes patients attending university of Gondar Hospital, Northwest Ethiopia. Frontiers in Public Health. 2018;6:81.
Ahuru RR, Akpojubaro EH. The Effects of illhealth and disabilities on labour force participation among nigerian households. Oradea
Journal of Business and Economics.
;5(2):8–19.
Afolalu OO, Akinwale OD, Makinde SO, Olawale SG, Folami RO, Orunmuyi IJ. Psychological Impact of Diabetic Care on Satisfaction and Quality of Life of Diabetes Patients Attending Endocrinology Clinic, LAUTECH Teaching
Hospital, Osun State, Southwest, Nigeria. Asian Journal of Medicine and Health [Internet]. 2021;19(9).
Daya R, Bayat Z, Raal F. Effects of diabetes mellitus on health-related quality of life at a tertiary hospital in South Africa: A cross-sectional study. South African Medical Journal. 2016;106(9):918–28.
Puspasari S, Farera DR. Quality of Life Among Patients with Type 2 Diabetic Mellitus in Outpatient Department, General Public Hospital, West Java. KnE Life Sciences. 2021;897–906.
Kalra S, Jena BN, Yeravdekar R. Emotional and psychological needs of people with diabetes. Indian journal of endocrinology and metabolism. 2018;22(5):696.
Mapa-Tassou C, Katte JC, MbaMaadjhou C, Mbanya JC. Economic impact of diabetes in Africa. Current diabetes reports. 2019;19(2):1–8.
Okoronkwo IL, Ekpemiro JN, Okwor EU, Okpala PU, Adeyemo FO. Economic burden and catastrophic cost among people living with type2 diabetes mellitus attending a tertiary health institution in south-east zone, Nigeria. BMC research notes. 2015;8(1):1–8.
Issa B, Baiyewu O. Quality of life of patients with diabetes mellitus in a Nigerian teaching hospital. Hong Kong Journal of Psychiatry. 2006;16(1).
Lima LR de, Funghetto SS, Volpe CRG, Santos WS, Funez MI, Stival MM. Quality of life and time since diagnosis of diabetes mellitus among the elderly. RevistaBrasileira de Geriatria e Gerontologia. 2018;21:176–85.
Thapa S, Pyakurel P, Baral DD, Jha N. Healthrelated quality of life among people living with type 2 diabetes: a community based crosssectional study in rural Nepal. BMC Public Health. 2019;19(1):1–6.
S t o j a n o v i æ M , C v e t a n o v i æ G ,
AnðelkoviæApostoloviæ M, Stojanoviæ D, Ranèiæ N. Impact of socio-demographic characteristics and long-term complications on quality of life in patients with diabetes mellitus. Central European journal of public health. 2018;26(2):104–10.
World Health Organization. A vision for primary health care in the 21st century: towards universal health coverage and the Sustainable Development Goals. World Health Organization; 2018.
Latunji O, Akinyemi O. Factors influencing health-seeking behaviour among civil servants in Ibadan, Nigeria. Annals of Ibadan postgraduate medicine. 2018;16(1):52–60.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2023 Research Journal of Health Sciences

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
Research Journal of Health Sciences journal is a peer reviewed, Open Access journal. The Journal subscribed to terms and conditions of Open Access publication. Articles are distributed under the terms of Creative Commons License (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0). (http://creativecommons.org/licences/by-nc-nd/4.0). All articles are made freely accessible for everyone to read, download, copy and distribute as long as appropriate credit is given and the new creations are licensed under the identical terms.

