Relationship between resilience, depression, stress and anxiety among nurses in a tertiary health institution in Nigeria.
Keywords:
Resilience, Nurses, depression, stress, anxietyAbstract
Background: This study determines the relationship between resilience, depression, stress and anxiety among professional nurses who are frontline workers.
Methodology: The study was conducted among nurses working in Lagos State University Teaching Hospital (LASUTH) Ikeja, Lagos State. The Connor-Davidson Resilience scale and Depression, Anxiety and Stress questionnaire administered to 360 nurses. Simple frequency, mean, standard deviation and Pearson correlation were used for the analysis.
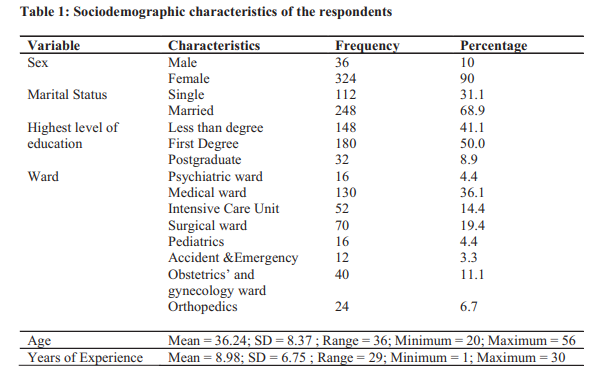
Results: The majority (90%) of the respondents was female and about two thirds of them were married. Overall summarized scores for the level of anxiety, depression and stress were 46.6%, 38.5% and 37.7% respectively. Resilience had statistically significant positive correlation with years of experience (r=0.160, p=0.002); negatively significant with stress (r = -0.281, p< 0.001) and negatively significant with anxiety (r = -0.210, p < 0.001). Depression was negatively significant with years of experience (r = 0.132, p = 0.013) while stress was positively significant with depression (r = 0.764, p< 0.001) and anxiety (r = 0.751, p < 0.001).
Conclusion: There is a need to organize programmes that will improve the resilience of professional nurses should be organized to reduce the effects of stress, anxiety and depression among nurses.
References
Poursadeghiyan M, Abbasi M, Mehri A, Hami M. Relationship Between Job Stress and Anxiety , Depression and Job Satisfaction in Nurses in Iran.The Social Sciences, 2016;11(9):2349–55.
Jordan TR, Khubchandani J, Wiblishauser M. The Impact of Perceived Stress and Coping
Adequacy on the Health of Nurses?: A Pilot Investigation. Nurs Res Pract, 2016;5(2)
Faremi F, Olatubi M, Adeniyi K, Salau O.
Assessment of occupational related stress among nurses in two selected hospitals in a city southwestern Nigeria. Int J Africa Nurs Sci.
0 1 9 ; 1 0 ( 2 ) : 6 8 – 7 3 . A v a i l a b l e
from:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijans.2019.01.00
Olabisi OI, Afolayan J, Oriola O, Ogunlade A, Olawoore S. Psychiatric nurses perspectives on causes and management of aggression in a Nigerian psychiatric hospital. AU J Heal Sci Biomed Res, 2019;1(1): 3-7
Olabisi OI, Ajibade BL, Ajao O, Ejidokun A, Oriola O. Experience and Attitude of Psychiatric Nurses toward Inpatient Aggression in a
Nigerian Psychiatric Hospital. Int J Caring Sci.
;12(3):1547–60. Available from:
http://ezproxy.umgc.edu/login?url=https://searc h.ebscohost.com/login.aspx?direct=true&db=cc m&AN=139544928&site=eds-live&scope=site
Johnston D, Ph D, Bell C, Sc M, Jones M, Ph D, et al. Stressors , Appraisal of Stressors , Experienced Stress and Cardiac Response?: A
Real-Time , Real-Life Investigation of Work
Stress in Nurses. Ann Behav Med,
;10(5):187–97.
Mohite N, Shinde M, Gulavani A. Occupational Stress among Nurses Working At Selected
Tertiary Care Hospitals. International Journal of Science and Research 2014;3(6):999–1005.
Mousavi SV, Ramezani M, Salehi I, Hossein AA. The Relationship between Burnout Dimensions and Psychological Symptoms ( Depression , Anxiety and Stress ) Among Nurses. J Holist Nurs Midwifery, 2017;27(2):37–43.
Olabisi OI, Ajiboye T, Azeez F, Ejidokun A, Yusuff J. Workplace Bullying and Mental Health of Clinical Nuses in a Federal Medical Hospital in Southwest, Nigeria. LAUTECH J Nurs. 2021;
(1):53-60
Akmal H, Halim M, Halim FW, Khairuddin R. Does Personality Influence Workplace Bullying and Lead to Depression Among Nurses. Psychology; 2019;53(2):3–12.
Shajan A, Nisha C. Anxiety and Depression among nurses working in a tertiary care hospital in South India.International Journal of Advances in Medicine, 2019; 6(5):1611-1615
Lin C, Liang H, Han C, Chen L, Hsieh C. Professional resilience among nurses working in
an overcrowded emergency department in Taiwan. Int Emerg Nurs. 2019;42(10):44–50.
A v a i l a b l e f r o m :
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ienj.2018.05.005
Brennan EJ. Towards resilience and wellbeing in nurses. Br J Nurs. 2017;26(1).
Obeidavi A, Elahi N, Saberipour B. Relationship between resilience and occupational stress among the faculty members of Ahvaz
Jundishapur University of Medical Sciences. Int J Biomed Public Heal. 2018;1(3):136–40.
Jafarizadeh H. Effect of resilience-based intervention on occupational stress among nurses.International Health Affair,
;15(9):159–63.
Olabisi OI, Dosumu T, Ademuyiwa G, Adeleke J,
Nathaniel O, Olabisi T. Depression, Anxiety, Stress and Social Support Among Pregnant Women Attending Antenatal Clinic in a Nigerian Teaching Hospital. Bayero J Nurs Heal Care. 2020;2(2).
Olabisi OI, Olorunfemi O, Bolaji A, Azeez FO, Olabisi TE, Azeez O. Depression, anxiety, stress and coping strategies among family members of patients admitted in intensive care unit in Nigeria. Int J Africa Nurs Sci. 2020;13 Available f r o m :
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijans.2020.100223
Aloba O, Olabisi O, Aloba T. The 10-Item Connor–Davidson Resilience Scale: Factorial Structure, Reliability, Validity, and Correlates Among Student Nurses in Southwestern Nigeria. J Am Psychiatr Nurses Assoc. 2016;22(1):43–51.
Hjemdal O, Vogel PA, Solem S, Hagen K, Stiles TC. The relationship between resilience and levels of anxiety, depression, and obsessivecompulsive symptoms in adolescents. Clin Psychol Psychother. 2011;18(4):314–21.
Maharaj S, Lees T, Lal S. Prevalence and Risk Factors of Depression , Anxiety , and Stress in a Cohort of Australian Nurses.Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019; 16(1)
Roberts NJ, Mcaloney-kocaman K, Lippiett K, Ray E, Welch L, Kelly C. Levels of resilience , anxiety and depression in nurses working in respiratory clinical areas during the COVID pandemic. Respir Med. 2020;176. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rmed.2020. 106219
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2023 Research Journal of Health Sciences

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
Research Journal of Health Sciences journal is a peer reviewed, Open Access journal. The Journal subscribed to terms and conditions of Open Access publication. Articles are distributed under the terms of Creative Commons License (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0). (http://creativecommons.org/licences/by-nc-nd/4.0). All articles are made freely accessible for everyone to read, download, copy and distribute as long as appropriate credit is given and the new creations are licensed under the identical terms.

