Kidney dysfunction and Mortality Risk in Hospitalized Covid-19 Patients: A large Covid-19 Centre Experience
Keywords:
COVID-19, eGFR, MortalityAbstract
Objective: Kidney dysfunction is common in patients infected with the coronavirus (COVID-19). The study’s objective was to determine the relationship between glomerular filtration rate and mortality in COVID-19 patients.
Methods: This is a retrospective cohort study of patients admitted into the COVID-19 isolation center from March 2020 through December 2021. The serum creatinine at admission was used to estimate the glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) using the CKD EpI method. The patients were categorized into 2 groups based on the eGFR (≥ or < 60ml/minute). The outcome was in-hospital mortality. Kaplan Meier survival plots and cox proportional modelling were employed in the data analysis.
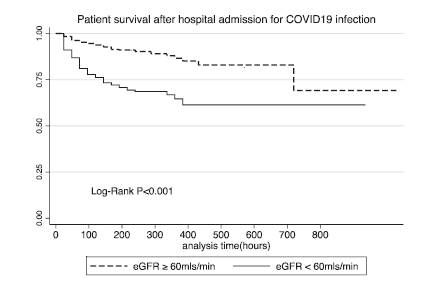
Results: A total of 623 patients were analysed. The mean age was 53.4±15.3 years, and 58.6% were male. An eGFR of < 60 ml/min was observed in 196 (31%) patients. A significantly higher number of deaths occurred among patients with eGFR <60ml/min (32% vs 10.5% (P<0.001). After adjusting for age, sex, disease severity, haemoglobin, ICU admission, and dialysis, the patients with reduced eGFR of (<60ml/min) were twice as likely to die than patients with eGFR ≥ 60mls/min (AHR 1.95, 95% CI 1.26-3.04, P = 0.003).
Conclusion: eGFR of < 60mls/min is associated with an increased risk of mortality in COVID-19 patients. This stresses the need for better recognition of renal dysfunction as a high-risk for mortality in COVID-19 infections.
References
Cucinotta D, Vanelli M. WHO Declares COVID-19 a Pandemic. Acta Biomed. 2020;91(1):157-60.
Huang C, Wang Y, Li X, Ren L, Zhao J, Hu Y, et al. Clinical features of patients infected with 2019 novel coronavirus in Wuhan, China. Lancet (London, England). 2020;395(10223):497-506.
Guan WJ, Ni ZY, Hu Y, Liang WH, Ou CQ, He JX, et al. Clinical Characteristics of Coronavirus Disease 2019 in China. N Engl J Med. 2020;382(18):1708-20.
Chan L, Chaudhary K, Saha A, Chauhan K, Vaid A, Zhao S, et al. AKI in Hospitalized Patients with COVID-19. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2021;32(1):151-60.
Russo E, Esposito P, Taramasso L, Magnasco L, Saio M, Briano F, et al. Kidney disease and all-cause mortality in patients with COVID-19 hospitalized in Genoa, Northern Italy. J Nephrol. 2021;34(1):173-83.
Ferlicot S, Jamme M, Gaillard F, Oniszczuk J, Couturier A, May O, et al. The spectrum of kidney biopsies in hospitalized patients with COVID-19, acute kidney injury, and/or proteinuria. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2021.
Pei G, Zhang Z, Peng J, Liu L, Zhang C, Yu C, et al. Renal Involvement and Early Prognosis in Patients with COVID-19 Pneumonia. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2020;31(6):1157-65.
Kolhe NV, Fluck RJ, Selby NM, Taal MW. Acute kidney injury associated with COVID-19: A retrospective cohort study. PLoS Med. 2020;17(10):e1003406-e.
Wang M, Xiong H, Chen H, Li Q, Ruan XZ. Renal Injury by SARS-CoV-2 Infection: A Systematic Review. Kidney Diseases. 2021;7(2):100-10.
Cheng Y, Luo R, Wang K, Zhang M, Wang Z, Dong L, et al. Kidney disease is associated with in-hospital death of patients with COVID-19. Kidney International. 2020;97(5):829-38.
Legrand M, Bell S, Forni L, Joannidis M, Koyner JL, Liu K, et al. Pathophysiology of COVID-19-associated acute kidney injury. Nature Reviews Nephrology. 2021;17(11):751-64.
Williamson EJ, Walker AJ, Bhaskaran K, Bacon S, Bates C, Morton CE, et al. Factors associated with COVID-19-related death using OpenSAFELY. Nature. 2020;584(7821):430-6.
Zheng X, Zhao Y, Yang L. Acute Kidney Injury in COVID-19: The Chinese Experience. Semin Nephrol. 2020;40(5):430-42.
Uribarri A, Núñez-Gil IJ, Aparisi A, Becerra-Muñoz VM, Feltes G, Trabattoni D, et al. Impact of renal function on admission in COVID-19 patients: an analysis of the international HOPE COVID-19 (Health Outcome Predictive Evaluation for COVID 19) Registry. Journal of Nephrology. 2020;33(4):737-45.
Levey AS, Stevens LA, Schmid CH, Zhang YL, Castro AF, 3rd, Feldman HI, et al. A new equation to estimate glomerular filtration rate. Ann Intern Med. 2009;150(9):604-12.
Elixhauser A, Steiner C, Harris DR, Coffey RM. Comorbidity measures for use with administrative data. Med Care. 1998;36(1):8-27.
van Walraven C, Austin PC, Jennings A, Quan H, Forster AJ. A modification of the Elixhauser comorbidity measures into a point system for hospital death using administrative data. Med Care. 2009;47(6):626-33.
Mirijello A, Piscitelli P, de Matthaeis A, Inglese M, D’Errico MM, Massa V, et al. Low eGFR Is a Strong Predictor of Worse Outcome in Hospitalized COVID-19 Patients. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2021;10(22):5224.
Cei F, Chiarugi L, Brancati S, Montini MS, Dolenti S, Di Stefano D, et al. Early reduction of estimated Glomerular Filtration Rate (eGFR) predicts poor outcome in acutely ill hospitalized COVID-19 patients firstly admitted to medical regular wards (eGFR-COV19 study). Biomed Pharmacother. 2022;153:113454.
Ibrahim OR TOT, Gbadamosi H , Musa Y , Aliu R , Bello SO , Alao MA , Suleiman MS , Adedoyin OT. Acute kidney injury in COVID–19: A single–center experience in Nigeria. . Anaesth pain intensive care. 2021;25(4):470-7.
Dolaama B, Konan, S.D., Diopoh, S.P., Moudachirou, M.A.,Tona, K.G., Amekoudi, E.Y.M., Tsevi, M.C.Yao, K.H. . COVID-19 Infection and Acute Kidney Injury: About 43 Cases Report Collected at the Nephrology Department of the Farah Polyclinic in Abidjan. OpenJournal of Nephrology, 12, 410-425. 2022;12:410-25.
Tannor EK. Challenges in Kidney Care in a Lower Middle Income Country During the COVID-19 Pandemic - the Ghanaian Perspective. Kidney Int Rep. 2021;6(8):2014-6.
Robbins-Juarez SY, Qian L, King KL, Stevens JS, Husain SA, Radhakrishnan J, et al. Outcomes for Patients With COVID-19 and Acute Kidney Injury: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Kidney Int Rep. 2020;5(8):1149-60.
Bravi F, Flacco ME, Carradori T, Volta CA, Cosenza G, De Togni A, et al. Predictors of severe or lethal COVID-19, including Angiotensin Converting Enzyme inhibitors and Angiotensin II Receptor Blockers, in a sample of infected Italian citizens. PLoS One. 2020;15(6):e0235248.
Denic A, Glassock RJ, Rule AD. Structural and Functional Changes With the Aging Kidney. Adv Chronic Kidney Dis. 2016;23(1):19-28.
Ogoina D, Mahmood D, Oyeyemi AS, Okoye OC, Kwaghe V, Habib Z, et al. A national survey of hospital readiness during the COVID-19 pandemic in Nigeria. PLoS One. 2021;16(9):e0257567.
Adejumo OA. Impact of COVID-19 pandemic on renal care services in Nigeria. Pan Afr Med J. 2020;35(Suppl 2):101.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2023 Research Journal of Health Sciences

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
Research Journal of Health Sciences journal is a peer reviewed, Open Access journal. The Journal subscribed to terms and conditions of Open Access publication. Articles are distributed under the terms of Creative Commons License (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0). (http://creativecommons.org/licences/by-nc-nd/4.0). All articles are made freely accessible for everyone to read, download, copy and distribute as long as appropriate credit is given and the new creations are licensed under the identical terms.

