Prevalence of Diabetes Mellitus in a Rural, Agrarian Community in South-South Nigeria
Keywords:
Diabetes mellitus, Hypertension, Nigeria, RuralAbstract
Background: Diabetes mellitus (DM) is a global public health threat, often associated with other co-morbidities with significant morbidities and mortality. The aim of this study was to determine the prevalence of DM in a rural agrarian community in Nigeria.
Methodology: This cross-sectional study, using quantitative methods, was carried out in Ayua community in Etsako West local government area of Edo state, South-South Nigeria. Structured questionnaire was intervieweradministered while socio-demographics, anthropometric data, blood pressure and weight measurements as well as random blood glucose were obtained from participants.
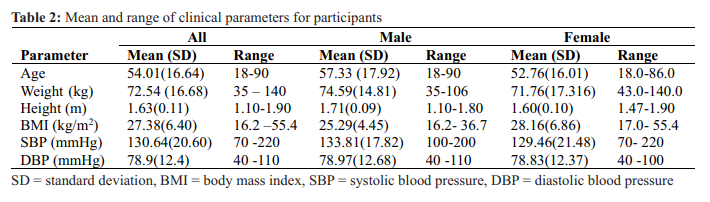
Findings: Two hundred and sixteen participants (58 males, 158 females) completed the study with a mean age of 54.2+16.4 years. Diabetes was found in 30 (13.9%) participants and undiagnosed in 40.0% while hypertension and obesity were found in 61(28.2%) and 57(26.4%) respectively. Diabetes was independently predicted by age > 50 years (OR = 5.7) and the presence of a family history of DM (OR = 43.0) with p < 0.001 each) but not by obesity (p=0.860), hypertension (p = 0.477) or family history of hypertension (p = 0.09).
Conclusion: Considering the high prevalence of DM and co-morbidities in this rural agrarian community, we recommend regular screening of adults for these conditions
References
Zimmet PZ, Magliano DJ, Herman WH, Shaw
JE. Diabetes: a 21st century challenge. Lancet
Diabetes Endocrinol 2014;2(1):56-64
World Health Organization. Diabetes.
http://www.who.int. Updated 8 June 2020.
Accessed 30 July 2020.
Chuhwak EK, Okeahialam BN, Ogbonna C,
Pam SD. Diabetes in elderly Nigerians: A
survey of a rural area in north-central Nigeria. J
Med Trop 2019; 21:51-5.
Ekpebegh C. Diabetes mellitus in Nigeria: the
past, present and future. World J Diabetes 2014;
:905–11.
Akinkugbe OO. Non-communicable diseases in
Nigeria-final report of a national survey. Lagos:
Federal Ministry of Health-National Expert
Committee on Non-Communicable Diseases;
p. 65-8.
Uloko AE, Musa BM, Ramalan MA, Gezawa
ID, Puepet FH, Uloko AT et al. Prevalence and
Risk Factors for Diabetes Mellitus in Nigeria: A
Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.
Diabetes Ther 2018; 9(3): 1307–1316.
Ohwovoriole AE, Kuti JA, Kabiawu SI. Casual
blood glucose levels and prevalence of
undiscovered diabetes mellitus in Lagos
metropolis Nigerians. Diabetes Res Clin Pract
; 4:153-8.
Dyck R, Karunanayake C, Pahwa P, Hagel L,
Lawson J, Rennie D et al. Prevalence, risk
factors and co-morbidities of diabetes among
adults in rural Saskatchewan: the influence of
farm residence and agriculture-related
exposures. BMC Public Health. 2013; 13: 7.
Qi L, Hu FB, Hu G. Genes, environment, and
interactions in prevention of type 2 diabetes: a
focus on physical activity and lifestyle changes.
Curr Mol Med. 2008; 8:519–532. 5.
National Population Commission of Nigeria [N Pop C]. Population and Housing Census Facts and Figures; 2006.
American Diabetes Association. Diabetes Care
; 33(Suppl 1): S62 – S69.
Chobanian A V, Bakris GL, Black HR, Cushman residents of a Nigerian ethnic group: The
WC, Green LA, Izzo JL et al. The seventh report Kalabaris in the Niger Delta region of south-
of the Joint National Committee on Prevention, south Nigeria. Greener J Med Sci.2012; 2:152-
Detection, Evaluation, and Treatment of high 156.
blood pressure: the JNC 7 report. JAMA.2003; 22. Ejim EC, Okafor CI, Emehi A, Mbah AU, Onyia
(19):2560-72. U, Egwuonwu T et al. Prevalence of
Sabir AA, Balarabe S, Sani AA, Isezuo SA, cardiovascular risk factors in the middle-aged
Bello KS, Jimoh AO et al Prevalence of diabetes and elderly population of a Nigerian population.
mellitus and risk factors among the suburban J Trop Med 2011; 2011:308687. doi:10.,1155/
population of North Western Nigeria. Sahel 2011/308687.
Med J 2017; 20(4): 168-172. 23. Okesina AB, Oparinde DP, Akindoyin KA,
Arugu GM, Maduka O. Risk factors for diabetes Erasmus RT. Prevalence of some risk factors of
mellitus among adult residents of a rural District coronary heart disease in a rural Nigerian
in Southern Nigeria: Implications for population. East Afr Med J. 1999; 76(4):
prevention and control. Niger J Clin Pract 2017; 212–216.
(12): 1544-1549. 24. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention
Alikor CA, Emem-Chioma PC. Epidemiology National Diabetes Fact Sheet: General
of diabetes and impaired fasting glucose in a Information and National Estimates on
rural community of Nigerian Niger Delta Diabetes in the United States, 2011. Atlanta,
region. Niger J Med 2015; 24 (2):114-124. Georgia, U.S. Department of Health and Human
Isara AR, Okundia PO. The burden of Services, Centers for Disease Control and
hypertension and diabetes mellitus in rural Prevention 2011.
communities in southern Nigeria. Pan Afr Med 25. American Diabetes Association. Standards of
J. 2015; 20: 103. Medical Care in Diabetes - 2012. Diabetes Care.
Toth G, Szabo D, Sandor GL. Rural-urban 2012; 35(3): 660.
disparities in the prevalence of diabetes and 26. Apidechkul, T. Prevalence and factors
diabetic eye complications in Hungary. associated with type 2 diabetes mellitus and
Spektrum Augenheilkd 2019. https://doi.org/ hypertension among the hill tribe elderly
1007/s00717-019-00433-6. populations in northern Thailand. BMC Public
Oladapo OO, Falase AO, Salako L, Sodiq O, Health 18, 694 (2018). https://doi.org/
Shoyinka K, Adedapo K. A prevalence of 10.1186/s12889-018-5607-2
cardiometabolic risk factors among a rural 27. Tsimihodimos V, Gonzalez-Villalpando C,
Yoruba south-western Nigerian population: a Meigs JB, Ferrannini E. Hypertension and
population-based survey. Cardiovasc J Afr diabetes co-prediction and time trajectories.
; 21 (1): 26–31. Hypertension 2018.71(3):422-428.
Onwubere BJC, Ejim EC, Okafor CI, Emehel A, 28. Sasai H, Sairenchi T, Iso H, Irie F, Otaka E,
Mbah AU, Onyia U et al. Pattern of blood Tanaka K. Relationship between obesity and
pressure indices among the residents of a rural incident diabetes in middle aged and older
community in south east Nigeria, Int J Japanese adults: The Ibaraki Prefectural Health
Hypertens 2011, 2011: 621074. Study. Mayo Clin Proc 2010; 85(1):36- 40.
Kadiri S, Walker O, Salako BL, Akinkugbe O. 29. Shivananda N, Kheleel S, Shivang S, Vashista
Blood pressure, hypertension and correlates in S, Rukaiya S, Safayah S et al. Investing the link
urbanized workers in Ibadan, Nigeria: a revisit. between benign prostatic hypertrophy, BMI,
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2023 Research Journal of Health Sciences

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
Research Journal of Health Sciences journal is a peer reviewed, Open Access journal. The Journal subscribed to terms and conditions of Open Access publication. Articles are distributed under the terms of Creative Commons License (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0). (http://creativecommons.org/licences/by-nc-nd/4.0). All articles are made freely accessible for everyone to read, download, copy and distribute as long as appropriate credit is given and the new creations are licensed under the identical terms.

