Assessing diagnostic variations and correlates of fasting blood glucose
Keywords:
Fasting blood glucose, diabetes, diagnostic, Delta State, hypertensionAbstract
Objective: To assess the diagnostic variables of blood glucose level among students of basic medical Sciencesof Delta State University, Abraka Nigeria.
Methods: A descriptive cross sectional survey on a total of one hundred and ten (110) students of the Faculty of Basic Medical Science, Delta State University, Abraka was conducted. Descriptive statistics was used to analyze the differences in the data collected. [
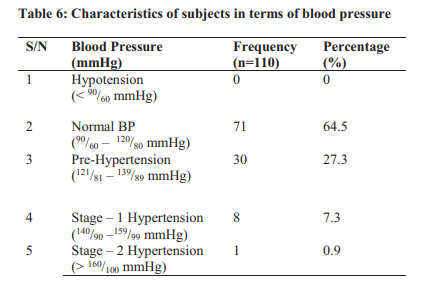
Results: The fasting blood glucose levels of 87.5% and 85% of the students had a normoglycemic level as indicated by the left and right thumb respectively. Also, a greater percentage (69.1%) of the students were between the age range 21 – 25. Furthermore, 72.7%, 76.4% and 64.5% of the students had normal weight, normal WHR and normal BP respectively.
Conclusion: There is no significant difference in the diagnostic assessment of blood glucose level using either right or left thumb.
References
Güemes M, Rahman SA, Hussain K. What is a normal blood glucose? Arch Dis Child. 2016; 101(6): 569-574.
Kaufman F. Role of the continuous glucose monitoring system in pediatric patients. Diabetes Technol Ther. 2000; 2(1): S49–52.
Goyal N, Kaur R, Sud A, Ghorpade N, Gupta M. Non diabetic and stress induced hyperglycemia [SIH] in orthopaedic practice: What do we know
so far? J Clin Diagn Res. 2014; 8(10): 1 - 3
American Diabetes Association (ADA).
Diagnosis and Classification of Diabetes Mellitus. Diabetes Care. 2010; 33(S1): 62 - 69.
Oputa RN, Chinenye S. Diabetes in Nigeria–a translational medicine approach. African Journal of Diabetes Medicine. 2015; 23(1):7-10
International Diabetes Federation (IDF). IDF Diabetes atlas, 7th ed, 2015.
Tabák AG, Herder C, Rathmann W, Brunner EJ, Kivimäki M. Prediabetes: A high-risk state for developing diabetes. Lancet. 2012; 379(9833): 2279–2290.
Oluwayemi IO, Brink SJ, Oyenusi EE, Oduwole
OA, Oluwayemi MA. Fasting Blood Glucose Profile among Secondary School Adolescents in Ado-Ekiti , Nigeria. 2015; 417859
Marliss EB, Vranic M. Intense exercise has unique effects on both insulin release and its roles in glucoregulation: implications for diabetes. Diabetes. 2002; 51(1): S271–283.
Vinutha S, Paul F, Raymond D, Adam R, Heather R, Nirubasini P, Matthew C, Elizabeth D, Timothy J. Effect of exercise intensity and blood glucose level on glucose requirements to maintain stable glycaemia during exercise in individuals with type 1 diabetes. Int J Pediatr Endocrinol. 2015; 2015(Suppl 1): O39. doi: 10.1186/1687-9856-2015-S1-O39. Epub 2015 Apr 28. PMCID: PMC4428871.
Dean D, Daugaard JR, Young ME, Saha A, Vavvas D, Asp S, Kiens B, Kim KH, Witters L, Richter EA, Ruderman N. Exercise diminishes the activity of acetyl-CoA carboxylase in human muscle. Diabetes. 2000; 49(8): 1295–1300
Wilmore JH, Green JS, Stanforth PR, Gagnon J, Rankinen T, Leon AS, Rao DC, Skinner JS, Bouchard C. Relationship of changes in Maximal and Submaximal Aerobic Fitness to Change in NIDD. Relationship of changes in maximal and submaximal aerobic fitness to changes in cardiovascular disease and non-insulindependent diabetes mellitus risk factors with endurance training: the HERITAGE Family Study. Metabolism. 2001; 50(11): 1255-1263
Vittal BG, Praveen G, Deepak P. A Study of Body Mass Index in Healthy Individuals and Its
Relationship with Fasting Blood Sugar. J Clin Diagnostic Res. 2010; 4(6): 3421-3424.
Innocent O, ThankGod OO, Sandra EO, Josiah IE. Correlation between body mass index and blood glucose levels among some Nigerian undergraduates. HOAJ Biol. 2013; 2(1):4.
Steppan CM, Bailey ST, Bhat S, Brown EJ, Banerjee RR, Wright CM, Patel HR, Ahima RS, Lazar MA. The hormone resistin links obesity to diabetes. Nature. 2001; 409(6818): 307-12
Veghari G, Sedaghat M, Joshaghani H,
Banihashem S, Moharloei P, Angizeh A, Tazik E, Moghaddami A, Hajian-Talaki K, ZahedPasha Y. The association of fasting blood glucose (FBG) and waist circumference in northern adults in Iran: a population based study. J. Diabetes Metab Disord. 2014; 13: 2
Fu SN, Luk W, Wong CK, Cheung KL.
Progression from impaired fasting glucose to type 2 diabetes mellitus among Chinese subjects with and without hypertension in a primary care setting. J Diabetes. 2014; 6:438–46.
Yan Q, Sun D, Li X, Chen G, Zheng Q, Li L, Gu C, Feng B. Association of Blood Glucose Level and Hypertension in Elderly Chinese Subjects: A Community Based Study. BMC Endocr Disord. 2016; 16: 40
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2023 Research Journal of Health Sciences

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
Research Journal of Health Sciences journal is a peer reviewed, Open Access journal. The Journal subscribed to terms and conditions of Open Access publication. Articles are distributed under the terms of Creative Commons License (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0). (http://creativecommons.org/licences/by-nc-nd/4.0). All articles are made freely accessible for everyone to read, download, copy and distribute as long as appropriate credit is given and the new creations are licensed under the identical terms.

