Pattern of presentation of ear, nose, throat, head and neck injury in a developing country
Keywords:
Ear, Nose, Otorhinolaryngology, Head, Neck, Injuries, Trauma, Developing countryAbstract
Objective: Ear, nose, throat, head and neck injuries are a common otorhinolaryngology disorder worldwide. This study aimed at determining the prevalence, sociodemographic features, aetiology, clinical presentation management and outcome of injuries to the ear, nose, throat, head and neck region.
Methods: This was a prospective study of patients with otorhinolaryngolology, head and neck injuries that presented at our tertiary health institution. Consented patients were studied between October 2015 and September 2017. Analysis of obtained data was done with SPSS version 16.0.
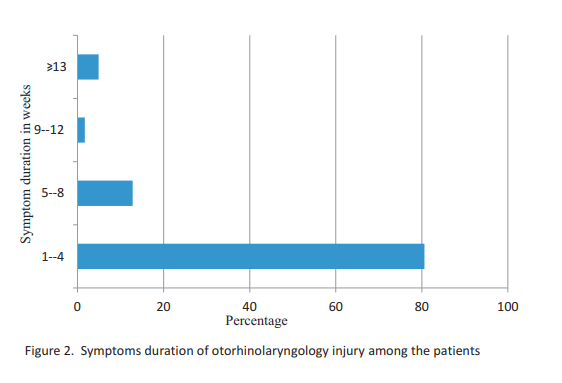
Results: The prevalence of ear, nose, throat, head and neck injury was 9.4%. There were 63.5% males 36.5% females with male to female ratio of 1.5:1. Foreign bodies' impaction was the commonest cause of injury in 32.3% followed by road traffic accidents in 19.8%. Commonest anatomical region were ear and nose in 49.7% and 28.5% respectively. Common clinical features among the patients were pain in 46.5%, bleeding in 37.8% and foreign bodies' impaction in 32.3%. Presentations for otorhinolaryngology care among the patients were common in 95.1% acute injury than 4.9% chronic injury (≥ 13 weeks). Commonest associated complications of the injuries were otitis media in 18.8% others were 14.9% otitis externa, 9.4% perforated tympanic membrane and 6.3% epistaxis. Pre-hospital treatment in the patients was 67.4%. Major treatment offered to the patients was conservative/medical therapy in 28.8%.
Conclusion: Ear, nose, throat, head and neck injuries are common in the otorhinolaryngology practice. Commonest causes are self inflicting foreign bodies' impaction and road traffic accident. Pre-hospital treatment among the patients was very high.
References
d a t a b a s e . 2 0 1 0 , / 2 0 1 1 .
https://www.google.com/search?q=Bugando+M edical+Centre+(BMC):+Medi Assessed on 23rd March, 2016
Gilyoma JM, Chalya PL: Endoscopic procedures for removal of foreign bodies of the aerodigestive tract: The Bugando Medical Centre experience. BMC Ear, Nose and Throat Disord 2011;11:2. https://doi.org/10.1186/1472-6815-11-2 Assessed on 16th October, 2016
Arif RK, Naseem U, Inayat U, Shah ED, Noor SK: Causes and complications of ear, nose and throat injuries in children. A study of 80 cases. J Med Sc. 2006;14 (1): 57-59.
Sogebi OA, Olaosun AO, Tobih JE, Adedeji TO, Adebola SO: Pattern of ear, nose and throat injuries in children at Ladoke Akintola University of technology teaching hospital, Osogbo, Nigeria. Afric J. Pediatr Surg. 2006; 3: 61-63.
Singh I, Gathwala G, Gathwala L, Yadav SPS, Wig U: Ear, Nose and Throat injuries in children. Pak J Otolaryngol. 1993; 9: 133-135.
Aremu SK, Alabi BS, Segun-Busari SW,
Omotoso SW: Audit of Pediatric ENT Injuries. Int J Biomed Sci. 2011; 7: 218-221.
Matilda I, Lucky O, Chibuike N: Ear, nose and throat injuries in a tertiary institution in Niger delta region Nigeria. J Med Res Prac. 2012; 1: 5962.
Arif RK, Saatea A: Ear, nose and throat injuries in children. Ayub med Coll Abbottabad. 2005; 17: 54-56.
Mohan D. Children injuries in India, extent of problem and strategies for control. Ind. J. Peads. 1986;53:171–176.
Soni NK, Sankhya N. Ear, Nose, Throat injuries in Children. Pakistan J Med Sci 1997;14(1):45–50.
Figueriedo RR, Azevedo AA, Kos AO, Tomita S: Complications of Ear, nose and throat foreign bodies. Braz J Otorhinolaryngol. 2008;74: 7-15.
Injury: A Leading Cause of the Global Burden of Disease. Geneva, Switzerland: World Health Organization; 2000.
Orji FT: Non-explosive blast injury of the tympanic membrane in Umuahia, Nigeria. Nig J Med. 2009; 18: 365-369.
Endican S, Garap JP, Dubey SP: Ear, nose and throat foreign body in Melanesian children: an analysis of 1037 cases. Int J Pediatr
Otorhinolaryngol. 2006;70: 1539-1545.
1016/j.ijporl.2006.03.018.
Okoye BC, Onotai LO: Foreign body in the nose. Niger J Med. 2006; 15: 301-304.
Fasunla J, Ibekwe T, Adeosun A: Preventable Risks in the Management of Aural Foreign Bodies in Western Nigeria. The Intern J
Otorhinolaryngol. 2007; 7(1).
Ette VF. Pattern of Ear, Nose and Throat Foreign Bodies seen in Uyo Nigeria. Ibom Medical Journal. 2012; 5(1). DOI: 41.203.67.54. 8
Daniilidis J,Symeonidis B,Triaridis K, Kouloulas A. Foreign body in the airways:review of 90 cases. Arch Otolaryngol 1977; 103: 570-573.
Biering-Sorensen M. Injuries or diseases of the ear; nose and throat encountered at a casualty department. A one-yearcase1oad. Ugeslcr Leager l990; 152:739-743.
Adegbiji WA, Aremu SK, Lasisi AO. Patients Barrier to Ear, Nose and Throat Surgical Care in Nigeria. Am Sci Research J Eng Tech and Sci (ASRJETS) (2017) ; 32(1): 96-104 .
Olajide TG, Gabriel-Alayode OE, Agboola SM, Fisch OE .Patterns of Ear, Nose and Throat Injuries in Ido Ekiti, Nigeria. Research journal of Ear, Nose and Throat. 2017; 1(5):1-5
Adegbiji WA, Olajide GT. Referred otalgia in Ekiti, Nigeria. European journal of pharmaceutical and medical research (EJPMR). 2017;4(11), 141-147.
Adegbiji WA, Olajide GT. Pattern of Otalgia in Ekiti, Nigeria. Am J Med Sci Med, 2017; 5(3): 5661.
Trunkey Donald D, Maull Kimball I: Prehospital Trauma care. Current Therapy of Trauma. Edited by: Trunkey Donald D, Lewis Frank R. 1999; Philadelphia: Mosby, 121-122. 4.
Liberman M, Mulder D, Lavoie A, Denis R, Sampalis JS: Multicenter Canadian study of prehospital trauma care. Ann Surg. 2003; 237 (2): 153-160.
Kang EG, Sharma GK, Lozano R: The global burden of injuries. Am J Public Health. 2000; 90: 523-526.
Hempel JM, Becker A, Müller J, Krause E,
Berghaus A, Braun T. Traumatic tympanic membrane perforations: clinical and audiometric findings in 198 patients. Otol Neurotol. 2012; 33(8):1357-62.
Gilyoma JM, Chalya PL. Ear,Nose and Throat injuries at Bugando Medical centre in North- western Tanzania: A five year prospective review of 456 cases: BMC Ear, Nose Throat Disord. 2013;13:4
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2023 Research Journal of Health Sciences

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
Research Journal of Health Sciences journal is a peer reviewed, Open Access journal. The Journal subscribed to terms and conditions of Open Access publication. Articles are distributed under the terms of Creative Commons License (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0). (http://creativecommons.org/licences/by-nc-nd/4.0). All articles are made freely accessible for everyone to read, download, copy and distribute as long as appropriate credit is given and the new creations are licensed under the identical terms.

