Connecting peptide (c-peptide) and the duration of diabetes mellitus amongst patients, at the Federal Medical Centre (FMC), Owerri, southeast, Nigeria
Abstract
Objective: C-peptide is derived from proinsulin and it is secreted in equimolar concentration with insulin. Plasma C-peptide is more stable than insulin and it provides an indirect measure of insulin secretory reserve and beta cell function. To determine relationship between C-peptide and duration of diabetes mellitus, age, body mass index, systolic blood pressure and diastolic blood pressure.
Methods: This is a cross-sectional study of type 2 diabetes mellitus patients attending Endocrine Clinic. Information such as age, sex, height, weight, blood pressure and duration of diabetes were obtained. Blood samples were taken for fasting serum C-peptide. Data was analysed using SPSS version 16.
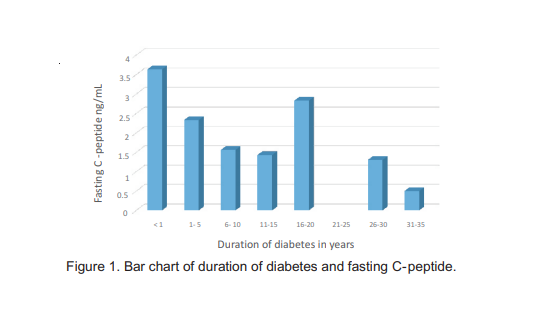
Results: Out of the 46 subjects recruited 23 (50%) were females and 23 (50%) were males. The mean age was 55.63 ± 14.7 years. Mean duration of diabetes for both sexes was 8 years with a range of 1 to 32 years. The mean BMI was 26.87 ± 5.00 kg/m2for males and 30.09 ± 4.32 Kg/m2 for females. The mean fasting serum C-peptide was 2.16 ± 1.41 ng/ml and there was no significant difference between males and females. There is statistically significant inverse correlation between C-peptide and duration of diabetes (r= -0.356, p= 0.015). Conversely there is a direct relationship between C-peptide and BMI (r=0.307, p=0.038).
Conclusion: Increasing duration of diabetes is associated with decreasing level of C-peptide and decreased beta cell secretory reserve.
References
Banting FG, Best CH. The internal secretions of the pancreas. J Lab Clin Med 1922; 7: 251-253
Bell G, Pictef RL, Rutter WJ, Cordel B, Tischer E, Goodman HM. Sequence of the human
insulin gene. Nature 1980; 284: 26-30
Palmer JP, Fleming GA, Greenbaum CJ, Herold KC, Jansa LD, Kolb H, et al. C-peptide is the appropriate outcome measure for type 1 diabetes clinical trials to preserve â - cell function. Report of an ADA Workshop, 21–22 October 2001. Diabetes. 2004;53:250–264
Li Y, Liu Y, Sato Y. The association between serum C-peptide levels and Bone Mineral
D e n s i t y . P L o S O N E 2 0 1 3 ;
:e83107.doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0083107 5. Steffes MW, Sibley S, Jackson M, Thomas W. Beta-cell function and development of diabetes related complications in diabetes and complication trial. Diabetes Care 2003; 26:832-
Marx N, Silbernagel G, Brandenburg V,
Burgmaier M, Kleber ME. C-peptide levels are associated with mortality and cardiovascular mortality in patients undergoing angiography. The LUDRIC Study. Diabetes Care, 2013; 36:708-714.
Abdullah BB, Patil BS, Thaseen A. Significance of C-peptide in type 2 diabetes- A study in North karmataka Population of India. Al Ameen J Med Sci. 2010; 31: 65-78.
Oli JM, Adeyema AA, Okafor GO, Ofoegbu EN, Onyenekwe B, Chukwuka CJ et al. Beta-cell function and response to treatment in Nigerians with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Res ClinPract. 2005; 69:196-204
Bakari AG, Onyemelukwe GC. Pancreatic beta cell function in type 2 diabetic Nigerian patients. Diabetes Inter. 2006; 14:21-23.
Sasaki TM, Gray RS, Ratner RE, Currier C, Aquino A, Barhyte Dy. Successful long-term kidney-pancreas transplant in diabetes patients with high C-peptide levels. Transplantation. 1998; 65:1510-1512.
Service FJ, Rizza RA, Zimmerman RR, Dyck
PJ, O Brien PC, Melton LJ. The classification of diabetes by clinical and C-peptide criteria. A prospective population-based study. Diabetes Care; 1997: 20:198-201
Stratton IM, Adler AI, Neil HA, Mathews DR, Manley SE, Cull CA et al. Association of glycemic macrovascular and microvascular complications of type 2 diabetes (UKPDS) prospective observational study. BMJ 2000; 321:405-412.
Nichols GA, Hillian TA, Brown JB. Progression from newly acquired impaired glucose to type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2007;30: 228-233.
Young EE, Chinenye S, Unachukwu CN. Beta cell response to mixed meal in Nigerian patients with type 2 diabetes. BMC Endocrine Disorders. 2012; 12:11
Siraj ES, Reddy SK, Scherbaum WA,
Abdulkadir J, Hammel JP, Faiman C. Basal and postglucagon C-peptide levels in Ethiopians with diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2002; 25:453-457.
Ferrannini E, Natali A, Bella P, Cavallo-Perin P, Lalic N, Mingrone. Insulin resistance and hypersecretion in obesity. Journal of Clinical Investigation. 1997; 100:1166-1173.
Yoon KH, Ko SH, Cho JH, Lee JM, Ann YB,
Song KH et al. Selective â-cell loss and â-cell expansion in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus in korea. Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism. 2003; 88:23002308.
Farsani SF, van der Aa MP, van der Vorst MMJ, Knibbe CAJ, de Boer A. Global trends in the incidence and prevalence of type 2 diabetes in children and adolescents: a systematic review and evaluation of methodological approaches. Diabetologia. 2013; 56: 1471-1488
Raji A, Seely EW, Arky RA, Simonson DC.
Body fat distribution and insulin resistance in healthy Asian Indians and Caucasians. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2001; 86: 5366-5371
DeFronzo RA. Banting Lecture. From the triumvirate to the ominous octet: a new paradigm for the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Care. 2009; 58: 773-795
Every NR, Boyko EJ, Keane EM, Marshal JA, Rewers M, Hamman RF. Blood pressure, insulin and C-peptide levels in San Luis Valley, Colorado. Diabetes Care. 1993;16:154350Farsani SF, van der Aa MP, van der Vorst MMJ, Knibbe CAJ, de Boer A. Global trends in the incidence and prevalence of type 2 diabetes in children and adolescents: a systematic review and evaluation of methodological approaches. Diabetologia. 2013; 56: 1471-1488
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2023 Research Journal of Health Sciences

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
Research Journal of Health Sciences journal is a peer reviewed, Open Access journal. The Journal subscribed to terms and conditions of Open Access publication. Articles are distributed under the terms of Creative Commons License (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0). (http://creativecommons.org/licences/by-nc-nd/4.0). All articles are made freely accessible for everyone to read, download, copy and distribute as long as appropriate credit is given and the new creations are licensed under the identical terms.

